Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax represses c-Myb-dependent transcription through activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and modulation of coactivator usage
- PMID: 11585920
- PMCID: PMC99912
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.21.7391-7402.2001
Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax represses c-Myb-dependent transcription through activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and modulation of coactivator usage
Abstract
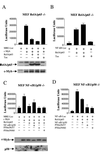
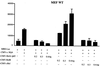
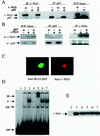
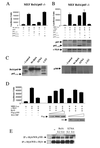
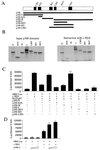
The proto-oncogene c-myb is essential for a controlled balance between cell growth and differentiation. Aberrant c-Myb activity has been reported for numerous human cancers, and enforced c-Myb transcription can transform cells of lymphoid origin by stimulating cellular proliferation and inhibiting apoptotic pathways. Here we demonstrate that activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by the HTLV-1 Tax protein leads to transcriptional inactivation of c-Myb. This conclusion was supported by the fact that Tax mutants unable to stimulate the NF-kappaB pathway could not inhibit c-Myb transactivating functions. In addition, inhibition of Tax-mediated NF-kappaB activation by coexpression of IkappaBalpha restored c-Myb transcription, and Tax was unable to block c-Myb transcription in a NEMO knockout cell line. Importantly, physiological stimuli, such as signaling with the cellular cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1 beta (IL-1beta), and lipopolysaccharide, also inhibited c-Myb transcription. These results uncover a new link between extracellular signaling and c-Myb-dependent transcription. The mechanism underlying NF-kappaB-mediated repression was identified as sequestration of the coactivators CBP/p300 by RelA. Interestingly, an amino-terminal deletion form of p300 lacking the C/H1 and KIX domains and unable to bind RelA retained the ability to stimulate c-Myb transcription and prevented NF-kappaB-mediated repression.
Figures
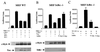
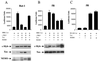
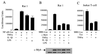
Similar articles
-
HTLV-I Tax transrepresses the human c-Myb promoter independently of its interaction with CBP or p300.Oncogene. 2000 Apr 20;19(17):2155-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203536. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10815807
-
Differential transcriptional activation by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax mutants is mediated by distinct interactions with CREB binding protein and p300.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Apr;18(4):2392-405. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.4.2392. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9528808 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of p53 by human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax requires activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and is dependent on p53 phosphorylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 May;20(10):3377-86. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.10.3377-3386.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10779327 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of I-kappaB kinase by the HTLV type 1 Tax protein: mechanistic insights into the adaptor function of IKKgamma.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Nov 1;16(16):1591-6. doi: 10.1089/08892220050193001. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 11080796 Review.
-
Cellular and viral protein interactions regulating I kappa B alpha activity during human retrovirus infection.J Leukoc Biol. 1997 Jul;62(1):82-92. doi: 10.1002/jlb.62.1.82. J Leukoc Biol. 1997. PMID: 9225998 Review.
Cited by
-
Tax relieves transcriptional repression by promoting histone deacetylase 1 release from the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(13):6735-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.13.6735-6743.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15194748 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell control by human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type 1.Int J Hematol. 2003 Nov;78(4):280-96. doi: 10.1007/BF02983552. Int J Hematol. 2003. PMID: 14686485 Review.
-
Suppression of PTEN expression by NF-kappa B prevents apoptosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;24(3):1007-21. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.3.1007-1021.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14729949 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin-induced inhibition of HTLV-I LTR activity is rescued by c-Myb.Retrovirology. 2007 Apr 3;4:24. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-4-24. Retrovirology. 2007. PMID: 17407584 Free PMC article.
-
RelB-p50 NF-kappa B complexes are selectively induced by cytomegalovirus immediate-early protein 1: differential regulation of Bcl-x(L) promoter activity by NF-kappa B family members.J Virol. 2002 Jun;76(11):5737-47. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.11.5737-5747.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11992002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akagi T, Ono H, Tsuchida N, Shimotohno K. Aberrant expression and function of p53 in T-cells immortalized by HTLV-1 Tax-1. FEBS Lett. 1997;406:263–266. - PubMed
-
- Beg A A, Sha W C, Bronson R T, Baltimore D. Constitutive NF-kappa B activation, enhanced granulopoiesis, and neonatal lethality in I kappa B alpha-deficient mice. Genes Dev. 1995;22:2736–2746. - PubMed
-
- Beg A A, Sha W C, Bronson R T, Gosh S, Baltimore D. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-kappa B. Nature. 1995;376:167–170. - PubMed
-
- Bender T P, Thompson C B, Kuehl W M. Differential expression of c-myb mRNA in murine B lymphomas by a block to transcription elongation. Science. 1987;237:1473–1476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
