The role of the hydrophilic Asn230 residue of the mu-opioid receptor in the potency of various opioid agonists
- PMID: 11588103
- PMCID: PMC1572970
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704263
The role of the hydrophilic Asn230 residue of the mu-opioid receptor in the potency of various opioid agonists
Abstract
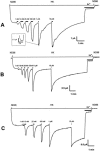
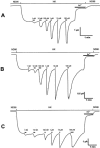
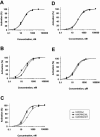
1. To investigate the effect of the hydrophilic Asn amino acid at position 230 of the human mu-opioid receptor (hMOR230) on the potency of various agonists, we mutated this residue to Thr and Leu (hMORN230T and hMORN230L respectively). 2. Taking advantage of the functional coupling of the opioid receptor with the heteromultimeric G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K(+) (GIRK1/GIRK2) channel, either the wild type hMOR or one of the mutated receptors (hMORN230L or hMORN230T) were functionally coexpressed with GIRK1/GIRK2 channels and a regulator of G-protein signalling (RGS4) in Xenopus laevis oocytes. 3. The two-microelectrode voltage clamp technique was used to measure the opioid receptor-activated GIRK1/GIRK2 channel responses. The potency of [D-Ala(2),N-MePhe(4),Gly(5)-ol]-enkephalin (DAMGO), remained unaffected as measured via hMORN230T and hMORN230L, while the potency of fentanyl and morphine significantly increased via these mutated receptors. 4. Our results are indicative for the existence of hydrophobic interactions between a methyl-group of the side chain of Thr or Leu on the one hand and the piperidine-ring of fentanyl and the hexene-ring of morphine on the other. The mutations also had no influence on the potency of morphine-6-glucuronide (M6G) and morphine-3-glucuronide (M3G). 5. We conclude that the hydrophilic side chain of Asn in position 230 is not involved in the formation of a H-bond with the aliphatic alcohol of morphine and that an enhancement of the potency of morphine and fentanyl can be explained by mutating this residue towards more hydrophobic amino acids.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction of p-fluorofentanyl on cloned human opioid receptors and exploration of the role of Trp-318 and His-319 in mu-opioid receptor selectivity.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Sep;294(3):1024-33. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000. PMID: 10945855
-
Serine 329 of the mu-opioid receptor interacts differently with agonists.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003 Mar;304(3):924-30. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.040113. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003. PMID: 12604666
-
Morphine-6beta-glucuronide and morphine-3-glucuronide, opioid receptor agonists with different potencies.Biochem Pharmacol. 2001 Nov 1;62(9):1273-82. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(01)00761-4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11705461
-
Effector antagonism by the regulators of G protein signalling (RGS) proteins causes desensitization of mu-opioid receptors in the CNS.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Jun;180(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-2248-9. Epub 2005 Apr 14. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15830230 Review.
-
Efficacy and ligand bias at the μ-opioid receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;169(7):1430-46. doi: 10.1111/bph.12222. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23646826 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular recognition of opioid receptor ligands.AAPS J. 2006 Mar 10;8(1):E126-37. doi: 10.1208/aapsj080115. AAPS J. 2006. PMID: 16584119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BEFORT K., TABBARA L., BAUSCH S., CHAVKIN C., EVANS C., KIEFFER B. The conserved asparate residue in the third putative transmembrane domain of the delta-opioid receptor is not the anionic counterpart for cationic opiate binding but is a constituent of the receptor binding site. Mol. Pharmacol. 1996;49:216–223. - PubMed
-
- BLACK S.D., MOULD D.R. Development of hydrophobicity parameters to analyze proteins which bear post- or cotranslational modifications. Anal. Biochem. 1991;193:72–82. - PubMed
-
- CHATURVEDI K., SHAHRESTANIFAR M., HOWELLS R.D. mu Opioid receptor: role for the amino terminus as a determinant of ligand binding affinity. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2000;76:64–72. - PubMed
-
- CHEN C., YIN J., RIEL J.K., DESJARLAIS R.L., RAVEGLIA L.F., ZHU J., LIU-CHEN L.Y. Determination of the amino acid residue involved in [3H]beta-funaltrexamine covalent binding in the cloned rat mu-opioid receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:21422–21429. - PubMed
-
- DERRICK I., NEILAN C.L., ANDES J., HUSBANDS S.M., WOODS J.H., TRAYNOR J.R., LEWIS J.W. 3-Deoxyclocinnamox: the first high-affinity nonpeptide mu-opioid antagonist lacking a phenolic hydroxyl group. J. Med. Chem. 2000;43:3348–3350. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

