Determination of effects of antiepileptic drugs on SNAREs-mediated hippocampal monoamine release using in vivo microdialysis
- PMID: 11588104
- PMCID: PMC1572980
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704285
Determination of effects of antiepileptic drugs on SNAREs-mediated hippocampal monoamine release using in vivo microdialysis
Abstract
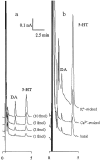
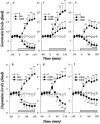
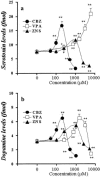
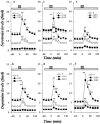
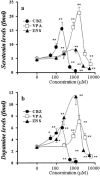
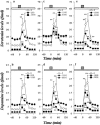
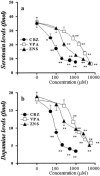
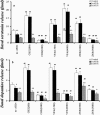
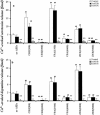
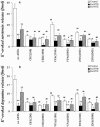
1. To elucidate possible mechanisms underlying the effects of carbamazepine (CBZ), valproate (VPA) and zonisamide (ZNS) on neurotransmitter exocytosis, the interaction between these three antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) and botulinum toxins (BoNTs) on basal, Ca(2+)- and K(+)-evoked release of dopamine (DA) and serotonin (5-HT) were determined by microdialysis in the hippocampus of freely moving rats. 2. Basal release of monoamine was decreased by pre-microinjection of the syntaxin inhibitor, BoNT/C, but only weakly affected by the synaptobrevin inhibitor, BoNT/B. Ca(2+)-evoked release was inhibited by BoNT/C selectively. K(+)-evoked release was reduced by BoNT/B predominantly and BoNT/C weakly. 3. Perfusion with low and high concentrations of CBZ and ZNS increased and decreased basal monoamine release, respectively. Perfusion with VPA increased basal 5-HT release concentration-dependently, whereas basal DA release was affected by VPA biphasic concentration-dependently, similar to CBZ and ZNS. This stimulatory action of AEDs on basal release was inhibited by BoNT/C predominantly. 4. Ca(2+)-evoked monoamine release was increased by low concentrations of CBZ, ZNS and VPA, but decreased by high concentrations. These effects of the AEDs on Ca(2+)-evoked release were inhibited by BoNT/C, but not by BoNT/B. 5. K(+)-evoked monoamine release was reduced by AEDs concentration-dependently. The inhibitory effect of these three AEDs on K(+)-evoked release was inhibited by BoNT/B, but not by BoNT/C. 6. These findings suggest that the therapeutic-relevant concentration of CBZ, VPA and ZNS affects exocytosis of DA and 5-HT, the enhancement of syntaxin-mediated monoamine release during resting stage, and the inhibition of synaptobrevin-mediated release during depolarizing stage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biphasic actions of topiramate on monoamine exocytosis associated with both soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors and Ca(2+)-induced Ca(2+)-releasing systems.Neuroscience. 2005;134(1):233-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.03.045. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 15961239
-
Pharmacological discrimination between effects of carbamazepine on hippocampal basal, Ca(2+)- and K(+)-evoked serotonin release.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Jun;133(4):557-67. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704104. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11399673 Free PMC article.
-
Exocytosis mechanism as a new targeting site for mechanisms of action of antiepileptic drugs.Life Sci. 2002 Dec 20;72(4-5):465-73. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(02)02283-x. Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 12467887 Review.
-
Effects of zonisamide on neurotransmitter release associated with inositol triphosphate receptors.Neurosci Lett. 2009 Apr 17;454(1):91-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.02.065. Epub 2009 Mar 3. Neurosci Lett. 2009. PMID: 19429061
-
[Methodological consideration in studying the exocytosis mechanisms using microdialysis].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2004 Aug;24(4):165-70. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15484814 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Carbamazepine Attenuates Astroglial L-Glutamate Release Induced by Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines via Chronically Activation of Adenosine A2A Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 30;20(15):3727. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153727. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31366130 Free PMC article.
-
Action of botulinum neurotoxins in the central nervous system: antiepileptic effects.Neurotox Res. 2006 Apr;9(2-3):197-203. doi: 10.1007/BF03033939. Neurotox Res. 2006. PMID: 16785118 Review.
-
Electrophysiology and pharmacology of striatal neuronal dysfunction induced by mitochondrial complex I inhibition.J Neurosci. 2008 Aug 6;28(32):8040-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1947-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18685029 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of mood stabilizers on marble-burying behavior in mice: involvement of GABAergic system.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Mar;226(2):295-305. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2904-9. Epub 2012 Oct 21. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23086022
-
Botulinum neurotoxin for pain management: insights from animal models.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Dec;2(12):2890-913. doi: 10.3390/toxins2122890. Epub 2010 Dec 21. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069581 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BOURGEOIS B.F.D.Valproic acid Clinical Use Antiepileptic drugs, Fourth edition 1995New York: Raven Press; 633–639.ed. Levy, R.H., Mattson, R.H. & Meldrum, B.S
-
- DESPLAND P.A. A retrospective study of 113 epileptic patients treated with sustained-release valproate. Epilepsia. 1994;35 Suppl 5:S99–S100. - PubMed
-
- DURING M.J., RYDER K.M., SPENCER D.D. Hippocampal GABA transporter function in temporal-lobe epilepsy. Nature. 1995;376:174–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

