Inhibition of interleukin-12 production by auranofin, an anti-rheumatic gold compound, deviates CD4(+) T cells from the Th1 to the Th2 pathway
- PMID: 11588111
- PMCID: PMC1572992
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704298
Inhibition of interleukin-12 production by auranofin, an anti-rheumatic gold compound, deviates CD4(+) T cells from the Th1 to the Th2 pathway
Abstract
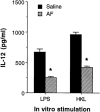
1. Interleukin-12 (IL-12) may play a central role in the development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis by driving the immune response towards T helper 1 (Th1) type responses characterized by high IFN-gamma and low IL-4 production. In this study we investigated the effect of auranofin (AF), an anti-rheumatic gold compound, on IL-12 production in mouse macrophages and dendritic cells, and studied whether AF-mediated inhibition of IL-12 production could regulate a cytokine profile of antigen (Ag)-primed CD4(+) Th cells. 2. Treatment with AF significantly inhibited IL-12 production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages and also in CD40L-stimulated dendritic cells. AF-pretreated macrophages reduced their ability to induce IFN-gamma and increased the ability to induce IL-4 in Ag-primed CD4(+) T cells. AF did not influence the cell surface expression of the class II MHC molecule and the costimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86. 3. Addition of recombinant IL-12 to cultures of AF-pretreated macrophages and CD4(+) T cells restored IFN-gamma production in Ag-primed CD4(+) T cells. 4. The in vivo administration of AF resulted in the inhibition of IL-12 production by macrophages stimulated in vitro with LPS or heat-killed Listeria monocytogenes (HKL), leading to the inhibition of Th1 cytokine profile (decreased IFN-gamma and increased IL-4 production) in Ag-primed CD4(+) T cells. 5. These findings may explain some known effects of AF including anti-rheumatic effects and the inhibition of encephalitogenicity, and point to a possible therapeutic use of AF in the Th1-mediated immune diseases such as autoimmune diseases.
Figures


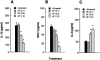
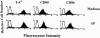
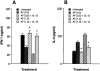
Similar articles
-
Curcumin inhibits Th1 cytokine profile in CD4+ T cells by suppressing interleukin-12 production in macrophages.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Sep;128(2):380-4. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702803. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10510448 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoid-mediated inhibition of interleukin-12 production in mouse macrophages suppresses Th1 cytokine profile in CD4(+) T cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Jun;130(3):581-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703345. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10821786 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of interleukin-12 production in mouse macrophages by berberine, a benzodioxoloquinolizine alkaloid, deviates CD4+ T cells from a Th2 to a Th1 response.Immunology. 2003 Jul;109(3):407-14. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01673.x. Immunology. 2003. PMID: 12807487 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-18 regulates both Th1 and Th2 responses.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:423-74. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.423. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11244043 Review.
-
IL-12 as a therapeutic target for pharmacological modulation in immune-mediated and inflammatory diseases: regulation of T helper 1/T helper 2 responses.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Jul;127(6):1295-304. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702689. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10455278 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selective inhibitory effects of 50-nm gold nanoparticles on mouse macrophage and spleen cells.J Immunotoxicol. 2016;13(2):198-208. doi: 10.3109/1547691X.2015.1035819. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Immunotoxicol. 2016. PMID: 25875326 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced and persistent levels of interleukin (IL)-17⁺ CD4⁺ T cells and serum IL-17 in patients with early inflammatory arthritis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 Nov;174(2):292-301. doi: 10.1111/cei.12167. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23815507 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing roles for CXCR3 signaling in central nervous system versus ocular inflammation mediated by the astrocyte-targeted production of IL-12.Am J Pathol. 2011 Nov;179(5):2346-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.07.041. Epub 2011 Sep 15. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21925471 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR3 modulates glial accumulation and activation in cuprizone-induced demyelination of the central nervous system.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Jun 16;11:109. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-109. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 24930935 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effects of Cucurbitane-Type Triterpenoids from Momordica charantia Fruit on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells.Molecules. 2021 Jul 23;26(15):4444. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154444. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ASNAGLI H., MURPHY K.M. Stability and commitment in T helper cell development. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2001;13:242–247. - PubMed
-
- ASTE-AMEZAGA M., D'ANDREA A., KUBIN M., TRINCHIERI G. Cooperation of natural killer cell stimulatory factor/interleukin-12 with other stimuli in the induction of cytokines and cytotoxic cell-associated molecules in human T and NK cells. Cell. Immunol. 1994;156:480–492. - PubMed
-
- ASTE-AMEZAGA M., MA X., SARTORI A., TRINCHIERI G. Molecular mechanisms of the induction of IL-12 and its inhibition by IL-10. J. Immunol. 1998;160:5936–5944. - PubMed
-
- BLODGETT R.C., HEUER M.A., PIETRUSKO R.G. Auranofin: a unique oral chrysotherapeutic agent. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1984;13:255–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

