Reduction of oxidative stress and AT1 receptor expression by the selective oestrogen receptor modulator idoxifene
- PMID: 11588112
- PMCID: PMC1572993
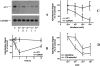
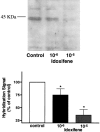
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704299
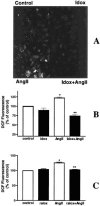
Reduction of oxidative stress and AT1 receptor expression by the selective oestrogen receptor modulator idoxifene
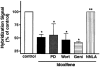
Abstract
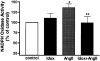
1. The beneficial vasoprotective effects of oestrogens are hampered by their side effects on secondary sexual organs. Selective oestrogen receptor modulators (SERM) such as idoxifene may exert beneficial vascular effects without influencing cancerogenesis in breast or uterus. 2. In order to investigate vascular effects of selective oestrogen receptor modulators, we examined the impact of idoxifene on production of reactive oxygen species as well as AT1 receptor expression in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC). 3. Idoxifene caused a concentration- and time-dependent down-regulation of AT1 receptor mRNA expression, as assessed by Northern analysis. The maximal effect was reached with 10 micromol l(-1) idoxifene after a 4 h incubation period (33+/-7% of control levels). Western blots showed a similar down-regulation of AT1 receptor protein to 36+/-11% of control levels. 4. Confocal laserscanning microscopy using the redox sensitive marker 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein (DCF) and measurement of NAD(P)H oxidase activity in cell homogenates revealed that idoxifene effectively blunted the angiotensin II-induced production of reactive oxygen species. 5. In order to investigate the signal transduction involved in SERM-induced modulation of AT1 receptor expression, VSMC were preincubation with PD98059, genistein, wortmannin, or N(omega)-Nitro-L-arginine. The results suggested that idoxifene caused AT1 receptor down-regulation through nitric oxide-dependent pathways. 6. In conclusion, idoxifene reduces angiotensin II-evoked oxidative stress in VSMC. This could in part be explained by idoxifene-induced down-regulation of AT1 receptor expression. These results demonstrate that the selective oestrogen receptor modulator idoxifene may exert beneficial vascular effects which could be useful for therapeutic regimen in postmenopausal women at risk for cardiovascular diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Negative feedback regulation of reactive oxygen species on AT1 receptor gene expression.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Oct;131(4):795-803. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703623. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11030730 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide stimulatory and endothelial protective effects of idoxifene, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, in the splanchnic artery of the ovariectomized rat.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Nov;295(2):786-92. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000. PMID: 11046119
-
C-reactive protein upregulates angiotensin type 1 receptors in vascular smooth muscle.Circulation. 2003 Apr 8;107(13):1783-90. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000061916.95736.E5. Epub 2003 Mar 17. Circulation. 2003. PMID: 12665485
-
Selective oestrogen receptor modulators/new antioestrogens: a clinical perspective.Cancer Treat Rev. 2004 Dec;30(8):695-706. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2004.04.003. Cancer Treat Rev. 2004. PMID: 15541579 Review.
-
Pathophysiological regulation of the AT1-receptor and implications for vascular disease.J Hypertens Suppl. 2006 Mar;24(1):S15-21. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000220402.53869.72. J Hypertens Suppl. 2006. PMID: 16601568 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 leads to the late development of angiotensin II-dependent glomerulosclerosis.Am J Pathol. 2006 Jun;168(6):1808-20. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.051091. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16723697 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen and estrogen receptors in cardiovascular oxidative stress.Pflugers Arch. 2013 May;465(5):739-46. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1247-7. Epub 2013 Feb 17. Pflugers Arch. 2013. PMID: 23417608 Review.
References
-
- CHRISTIANSEN C. Hormone replacement therapy and osteoporosis. Maturitas. 1996;23:S71–S76. - PubMed
-
- COLDITZ G.A., WILLETT W.C., STAMPFER M.J., ROSNER B., SPEIZER F.E., HENNEKENS C.H. Menopause and the risk of coronary heart disease in women. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987;316:1105–1110. - PubMed
-
- DARLEY-USMAR V.M., MCANDREW J., PATEL R., MOELLERING D., LINCOLN T.M., JO H., CORNWELL T., DIGERNESS S., WHITE C.R. Nitric oxide, free radicals and cell signalling in cardiovascular disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1997;25:925–929. - PubMed
-
- DELMAS P.D., BJARNASON N.H., MITLAK B.H., RAVOUX A.C., SHAH A.S., HUSTER W.J., DRAPER M., CHRISTIANSEN C. Effects of raloxifene on bone mineral density, serum cholesterol concentrations, and uterine endometrium in postmenopausal women. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;337:1641–1647. - PubMed
-
- FIGTREE G.A., LU Y., WEBB C.M., COLLINS P. Raloxifene acutely relaxes rabbit coronary arteries in vitro by an estrogen receptor-dependent and nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Circulation. 1999;100:1095–1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

