Increased contractile response to 5-hydroxytryptamine1-receptor stimulation in pulmonary arteries from chronic hypoxic rats: role of pharmacological synergy
- PMID: 11588116
- PMCID: PMC1572973
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704273
Increased contractile response to 5-hydroxytryptamine1-receptor stimulation in pulmonary arteries from chronic hypoxic rats: role of pharmacological synergy
Abstract
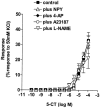
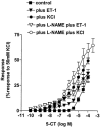
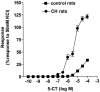
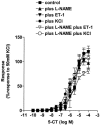
1. 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)(1)-receptor-induced contraction is enhanced, or uncovered, by elevated vascular tone in many arteries including pulmonary arteries. In hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension, the endogenous tone of pulmonary arteries is elevated and this may contribute to increased 5-HT(1)-receptor-induced contraction. Here we investigate the influence of vascular tone induced by endothelin-1 (ET-1), neuropeptide Y (NPY), KCl, 4-aminopyridine (inactivator of K(v) channels, 4-AP) or the calcium ionophore A23187 on contractile responses to the 5-HT(1)-receptor agonist 5-carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT) in small muscular pulmonary arteries from control rats and rats exposed to chronic hypoxia. The influence of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 100 microM) was also studied. These conditions were chosen to mimic those that influence pulmonary vascular tone in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. 2. In control rat small pulmonary arteries, only high concentrations of 5-CT (>1 microM) induced vasoconstriction. Tone induced by NPY, 4-AP and A23187 had no effect on responses to 5-CT whilst responses to 5-CT were increased by ET-1- and KCl-induced tone. In the presence of L-NAME these responses to 5-CT were enhanced further. 3. Responses to 5-CT were enhanced 3 - 4 fold in small pulmonary arteries from hypoxia-exposed, pulmonary hypertensive rats and neither L-NAME nor increasing tone with NPY, 4-AP, A23187, ET-1 or KCl had any further effect on responses to 5-CT. 4. The results suggest that inhibition of nitric oxide synthase combined with KCl- or ET-1-induced vascular tone potentiates responses to 5-HT(1)-receptor-induced contraction in pulmonary arteries in a synergistic fashion and this mimics the effects of chronic hypoxic exposure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors mediating vasoconstriction in pulmonary arteries from control and pulmonary hypertensive rats.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Nov;119(5):917-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15760.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8922741 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of applied tension and nitric oxide on responses to endothelins in rat pulmonary resistance arteries: effect of chronic hypoxia.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Mar;123(5):991-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701682. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9535030 Free PMC article.
-
5-hydroxytryptamine receptors mediating vasoconstriction and vasodilation in perinatal and adult rabbit small pulmonary arteries.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Sep;125(1):69-78. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702055. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9776346 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT moduline: an endogenous inhibitor of 5-HT(1B/1D)-mediated contraction in pulmonary arteries.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Mar;138(5):795-800. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705123. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12642380 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of pulmonary hypertension on vasoconstrictor responses to endothelin-1 and sarafotoxin S6C and on inherent tone in rat pulmonary arteries.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1995 Nov;26(5):822-30. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199511000-00020. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 8637198
Cited by
-
A Sex-Specific MicroRNA-96/5-Hydroxytryptamine 1B Axis Influences Development of Pulmonary Hypertension.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015 Jun 15;191(12):1432-42. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201412-2148OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015. PMID: 25871906 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV4 channel contributes to serotonin-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction and the enhanced vascular reactivity in chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Oct 1;305(7):C704-15. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00099.2013. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23739180 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term maternal hypoxia: the role of extracellular Ca2+ entry during serotonin-mediated contractility in fetal ovine pulmonary arteries.Reprod Sci. 2011 Oct;18(10):948-62. doi: 10.1177/1933719111401660. Reprod Sci. 2011. PMID: 21960509 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of propofol and etomidate on normoxic and chronically hypoxic pulmonary artery.BMC Anesthesiol. 2006 Mar 3;6:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2253-6-2. BMC Anesthesiol. 2006. PMID: 16515695 Free PMC article.
-
Maladaptive Pulmonary Vascular Responses to Chronic Sustained and Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia in Rat.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Dec 27;11(1):54. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010054. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BRINK C., CERRINA C., LABAT C., VERLEY J., BENVENISTE J. The effect of contractile agonists on isolated pulmonary arterial and venous muscle preparations derived from patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Am. Rev. Resp. Dis. 1988;137:A106.
-
- CHRISTMAN B.W. Lipid mediator dysregulation in primary pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 1998;114:205S–207S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

