Systemic ETA receptor antagonism with BQ-123 blocks ET-1 induced forearm vasoconstriction and decreases peripheral vascular resistance in healthy men
- PMID: 11588120
- PMCID: PMC1572995
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704304
Systemic ETA receptor antagonism with BQ-123 blocks ET-1 induced forearm vasoconstriction and decreases peripheral vascular resistance in healthy men
Abstract
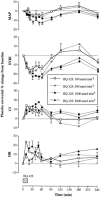
1. The effect on systemic haemodynamics of BQ-123, a selective endothelin A (ETA) receptor antagonist, was investigated in healthy men by giving, on separate occasions, ascending intravenous doses of 100, 300, 1000 and 3000 nmol min(-1) BQ-123, each for 15 min, in a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. The response of forearm blood flow to brachial artery infusion of endothelin-1 (ET-1; 5 pmol min(-1) for 90 min) was also studied using bilateral forearm plethysmography, after systemic pre-treatment, on separate occasions, with one of two doses of BQ-123 (300 and 1000 nmol min(-1) for 15 min) or placebo. 2. Systemic BQ-123 dose-dependently decreased systemic vascular resistance (P<0.01 for all doses vs placebo) and mean arterial pressure (P<0.05 for 300 nmol min(-1) and P<0.01 for 1000 and 3000 nmol min(-1)) during the 60 min following infusion. There were concurrent increases in heart rate and cardiac index. BQ-123, when infused systemically for 15 min, appeared to reach a maximum effect at 1000 nmol min(-1). 3. Intra-brachial ET-1 infusion, after pre-treatment with placebo, caused a slow onset progressive forearm vasoconstriction without systemic effects. This vasoconstriction was attenuated by pre-treatment with BQ-123 at 300 nmol min(-1) and abolished by BQ-123 at 1000 nmol min(-1) (P<0.01 vs placebo). 4. These effects occurred at concentrations of BQ-123 in the plasma (510+/-64 nmol l(-1)) that were ETA receptor selective, and were not accompanied by an increase in plasma ET-1 that would have indicated ETB receptor blockade. 5. We conclude that ETA-mediated vascular tone contributes to the maintenance of basal systemic vascular resistance and blood pressure in healthy men.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Action of the endothelin receptor (ETA) antagonist BQ-123 on forearm blood flow in young normotensive subjects.Clin Sci (Lond). 2002 Jun;102(6):661-6. Clin Sci (Lond). 2002. PMID: 12049621 Clinical Trial.
-
Altered peripheral vascular responses to exogenous and endogenous endothelin-1 in patients with well-compensated cirrhosis.Hepatology. 2001 Apr;33(4):826-31. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.23502. Hepatology. 2001. PMID: 11283846
-
Systemic endothelin receptor blockade decreases peripheral vascular resistance and blood pressure in humans.Circulation. 1996 May 15;93(10):1860-70. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.93.10.1860. Circulation. 1996. PMID: 8635265 Clinical Trial.
-
Endothelin in the pulmonary circulation with special reference to hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction.Scand Cardiovasc J Suppl. 1997;46:1-40. Scand Cardiovasc J Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9265559 Review.
-
Endothelin receptor antagonists in congestive heart failure: a new therapeutic principle for the future?J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001 May;37(6):1493-505. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(01)01210-4. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001. PMID: 11345356 Review.
Cited by
-
Vasodilator effects of the endothelin ET receptor selective antagonist BMS-193884 in healthy men.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Dec;60(6):611-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02503.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16305585 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical trials of endothelin antagonists in heart failure: publication is good for the public health.Heart. 2007 Jan;93(1):2-4. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2006.089250. Heart. 2007. PMID: 17170334 Free PMC article.
-
Acute endothelin A receptor antagonism improves pulmonary and systemic haemodynamics in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension that is primary or autoimmune and related to congenital heart disease.Heart. 2003 Oct;89(10):1221-6. doi: 10.1136/heart.89.10.1221. Heart. 2003. PMID: 12975426 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelin receptor type B: structure, function and dysregulation in vascular disease.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Jul 15;84(2):147-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.03.020. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22484314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Measurement of plasma endothelin-1 concentration in healthy horses and horses with cardiac disease during rest and after exercise.J Vet Med Sci. 2019 Feb 28;81(2):263-268. doi: 10.1292/jvms.18-0325. Epub 2018 Dec 28. J Vet Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30606891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ARAI H., HORI S., ARAMORI I., OHKUBO H., NAKANISHI S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990;348:730–732. - PubMed
-
- BENJAMIN N., CALVER A., COLLIER J., ROBINSON B., VALLANCE P., WEBB D. Measuring forearm blood flow and interpreting the responses to drugs and mediators. Hypertension. 1995;25:918–923. - PubMed
-
- CLOZEL M., GRAY G.A., BREU V., LOFFLER B., OSTERWALDER R. The endothelin ETB receptor mediates both vasodilatation and vasoconstriction in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992;186 - PubMed
-
- DE NUCCI G., THOMAS R., D'ORLEANS-JUSTE J.P., ANTUNES E., WALDER C., WARNER T.D., VANE J.R. Pressor effects of circulating endothelin are limited by its removal in the pulmonary circulation and by the release of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1988;85:9797–9800. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

