Effects of S-2474, a novel nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, on amyloid beta protein-induced neuronal cell death
- PMID: 11588123
- PMCID: PMC1572969
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704261
Effects of S-2474, a novel nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, on amyloid beta protein-induced neuronal cell death
Abstract
1. The accumulation of amyloid beta protein (Abeta) in the brain is a characteristic feature of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Clinical trials of AD patients with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) indicate a clinical benefit. NSAIDs are presumed to act by suppressing inhibiting chronic inflammation in the brain of AD patients. 2. In the present study, we investigated effects of S-2474 on Abeta-induced cell death in primary cultures of rat cortical neurons. 3. S-2474 is a novel NSAID, which inhibits cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) and contains the di-tert-butylphenol antioxidant moiety. S-2474 significantly prevented neurons from Abeta(25 - 35)- and Abeta(1 - 40)-induced cell death. S-2474 ameliorated Abeta-induced apoptotic features such as the condensation of chromatin and the fragmentation of DNA completely. 4. Prior to cell death, Abeta(25 - 35) generated prostaglandin D(2) (PGD(2)) and free radicals from neurons. PGD(2) is a product of cyclo-oxygenase (COX), and caused neuronal cell death. 5. S-2474 significantly inhibited the Abeta(25 - 35)-induced generation of PGD(2) and free radicals. 6. The present cortical cultures contained little non-neuronal cells, indicating that S-2474 affected neuronal survival directly, but not indirectly via non-neuronal cells. Both an inhibitory effect of COX-2 and an antioxidant effect might contribute to the neuroprotective effects of S-2474. 7. In conclusion, S-2474 exhibits protective effects against neurotoxicity of Abeta. Furthermore, the present study suggests that S-2474 may possess therapeutic potential for AD via ameliorating degeneration in neurons as well as suppressing chronic inflammation in non-neuronal cells.
Figures

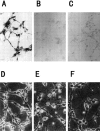
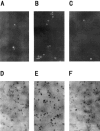
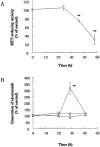

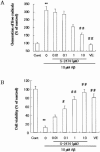
References
-
- ABDEL-HALIM M.S., HAMBERG M., SJÖQUIST, ÄNGGÅRD E. Identification of prostaglandin in homogenates of rat brain. Prostaglandin. 1977;14:633–643. - PubMed
-
- ASAKURA K., KANEMASA T., MINAGAWA K., KAGAWA K., NINOMIYA M. The nonpeptide α-eudesmol from Juniperus virginiana Linn. (Cupressaceae) inhibits ω-agatoxin IVA-sensitive Ca2+ currents and synaptosomal 45Ca2+ uptake. Brain Res. 1999;823:169–176. - PubMed
-
- BEHL C., DAVIS J.B., COLE G.M., SCHUBERT D. Vitamin E protects nerve cells from amyloid β protein toxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992;186:944–950. - PubMed
-
- BEHL C., DAVIS J.B., LESLEY R., SCHUBERT D. Hydrogen peroxide mediates amyloid β protein toxicity. Cell. 1994;77:817–827. - PubMed
-
- CHACON E., ACOSTA D. Mitochondrial regulation of superoxide by Ca2+: an alternate mechanism for the cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1991;107:117–128. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

