Opposing changes in phosphorylation of specific sites in synapsin I during Ca2+-dependent glutamate release in isolated nerve terminals
- PMID: 11588168
- PMCID: PMC6763853
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-20-07944.2001
Opposing changes in phosphorylation of specific sites in synapsin I during Ca2+-dependent glutamate release in isolated nerve terminals
Abstract
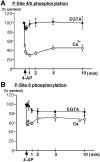
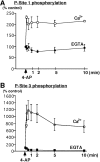
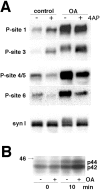
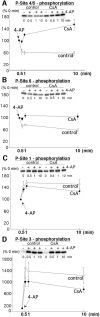
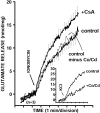
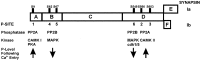
Synapsins are major neuronal phosphoproteins involved in regulation of neurotransmitter release. Synapsins are well established targets for multiple protein kinases within the nerve terminal, yet little is known about dephosphorylation processes involved in regulation of synapsin function. Here, we observed a reciprocal relationship in the phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of the established phosphorylation sites on synapsin I. We demonstrate that, in vitro, phosphorylation sites 1, 2, and 3 of synapsin I (P-site 1 phosphorylated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase; P-sites 2 and 3 phosphorylated by Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II) were excellent substrates for protein phosphatase 2A, whereas P-sites 4, 5, and 6 (phosphorylated by mitogen-activated protein kinase) were efficiently dephosphorylated only by Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase 2B-calcineurin. In isolated nerve terminals, rapid changes in synapsin I phosphorylation were observed after Ca(2+) entry, namely, a Ca(2+)-dependent phosphorylation of P-sites 1, 2, and 3 and a Ca(2+)-dependent dephosphorylation of P-sites 4, 5, and 6. Inhibition of calcineurin activity by cyclosporin A resulted in a complete block of Ca(2+)-dependent dephosphorylation of P-sites 4, 5, and 6 and correlated with a prominent increase in ionomycin-evoked glutamate release. These two opposing, rapid, Ca(2+)-dependent processes may play a crucial role in the modulation of synaptic vesicle trafficking within the presynaptic terminal.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hispidulin inhibits the release of glutamate in rat cerebrocortical nerve terminals.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Sep 1;263(2):233-43. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.06.015. Epub 2012 Jul 1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22759588
-
Localized Ca2+ entry preferentially effects protein dephosphorylation, phosphorylation, and glutamate release.J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1983-9. J Biol Chem. 1992. PMID: 1309806
-
Calcineurin-mediated protein dephosphorylation in brain nerve terminals regulates the release of glutamate.J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 23;269(38):23817-23. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 7522234
-
New aspects of neurotransmitter release and exocytosis: dynamic and differential regulation of synapsin I phosphorylation by acute neuronal excitation in vivo.J Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Sep;93(1):22-9. doi: 10.1254/jphs.93.22. J Pharmacol Sci. 2003. PMID: 14501147 Review.
-
Synapsin Isoforms and Synaptic Vesicle Trafficking.Mol Cells. 2015 Nov;38(11):936-40. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2015.0233. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Mol Cells. 2015. PMID: 26627875 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Relapse to cocaine-seeking after abstinence is regulated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A in the prefrontal cortex.Addict Biol. 2014 Jan;19(1):77-86. doi: 10.1111/adb.12043. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Addict Biol. 2014. PMID: 23461423 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF/TrkB signalling, in cooperation with muscarinic signalling, retrogradely regulates PKA pathway to phosphorylate SNAP-25 and Synapsin-1 at the neuromuscular junction.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jul 23;22(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01735-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39044222 Free PMC article.
-
Role of calcineurin in nicotine-mediated locomotor sensitization.J Neurosci. 2007 Aug 8;27(32):8571-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2601-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17687035 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of neurotransmitter release by the second messenger-activated protein kinases: implications for presynaptic plasticity.Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Jan;105(1):69-84. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.10.012. Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15626456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of synaptojanin 1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at synapses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 13;101(2):546-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307813100. Epub 2004 Jan 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14704270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi DR, Gomez N, Moorhead G, Lewis T, Keyse SM, Cohen P. Inactivation of p42 MAP kinase by protein phosphatase 2A and a protein tyrosine phosphatase, but not CL100, in various cell lines. Curr Biol. 1995;5:283–295. - PubMed
-
- Bähler M, Greengard P. Synapsin I bundles F-actin in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Nature. 1987;326:704–707. - PubMed
-
- Benfenati F, Valtorta F, Bahler M, Greengard P. Synapsin I, a neuron-specific phosphoprotein interacting with small synaptic vesicles and F-actin. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1989;13:1007–1021. - PubMed
-
- Benfenati F, Neyroz P, Bahler M, Masotti L, Greengard P. Time-resolved fluorescence study of the neuron-specific phosphoprotein synapsin I. Evidence for phosphorylation-dependent conformational changes. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:12584–12595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
