GABA(B2) is essential for g-protein coupling of the GABA(B) receptor heterodimer
- PMID: 11588177
- PMCID: PMC6763845
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-20-08043.2001
GABA(B2) is essential for g-protein coupling of the GABA(B) receptor heterodimer
Abstract
GABA(B) receptors are unique among G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in their requirement for heterodimerization between two homologous subunits, GABA(B1) and GABA(B2), for functional expression. Whereas GABA(B1) is capable of binding receptor agonists and antagonists, the role of each GABA(B) subunit in receptor signaling is unknown. Here we identified amino acid residues within the second intracellular domain of GABA(B2) that are critical for the coupling of GABA(B) receptor heterodimers to their downstream effector systems. Our results provide strong evidence for a functional role of the GABA(B2) subunit in G-protein coupling of the GABA(B) receptor heterodimer. In addition, they provide evidence for a novel "sequential" GPCR signaling mechanism in which ligand binding to one heterodimer subunit can induce signal transduction through the second partner of a heteromeric complex.
Figures

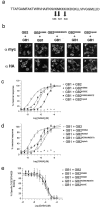
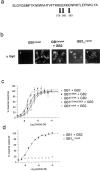





References
-
- AbdAlla S, Lother H, Quitterer U. AT1-receptor heterodimers show enhanced G-protein activation and altered receptor sequestration. Nature. 2000;407:94–98. - PubMed
-
- Barton GJ. ALSCRIPT: a tool to format multiple sequence alignments. Protein Eng. 1993;6:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Bowen WP, Jerman JC. Nonlinear regression using spreadsheets. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995;16:413–417. - PubMed
-
- Bowery NG. GABAB receptor pharmacology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:109–147. - PubMed
-
- Calver AR, Robbins MJ, Cosio C, Rice SQJ, Babbs AJ, Hirst WD, Boyfield I, Wood MD, Russell RB, Price GW, Couve A, Moss SJ, Pangalos MN. The C-terminal domains of the GABAB receptor subunits mediate intracellular trafficking, but are not required for receptor signaling. J Neurosci. 2001;21:1203–1210. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
