Nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA mutations define a spectrum of autosomal dominant macrothrombocytopenias: May-Hegglin anomaly and Fechtner, Sebastian, Epstein, and Alport-like syndromes
- PMID: 11590545
- PMCID: PMC1274350
- DOI: 10.1086/324267
Nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA mutations define a spectrum of autosomal dominant macrothrombocytopenias: May-Hegglin anomaly and Fechtner, Sebastian, Epstein, and Alport-like syndromes
Abstract
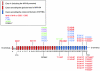
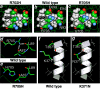
May-Hegglin anomaly (MHA) and Fechtner (FTNS) and Sebastian (SBS) syndromes are autosomal dominant platelet disorders that share macrothrombocytopenia and characteristic leukocyte inclusions. FTNS has the additional clinical features of nephritis, deafness, and cataracts. Previously, mutations in the nonmuscle myosin heavy chain 9 gene (MYH9), which encodes nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA (MYHIIA), were identified in all three disorders. The spectrum of mutations and the genotype-phenotype and structure-function relationships in a large cohort of affected individuals (n=27) has now been examined. Moreover, it is demonstrated that MYH9 mutations also result in two other FTNS-like macrothrombocytopenia syndromes: Epstein syndrome (EPS) and Alport syndrome with macrothrombocytopenia (APSM). In all five disorders, MYH9 mutations were identified in 20/27 (74%) affected individuals. Four mutations, R702C, D1424N, E1841K, and R1933X, were most frequent. R702C and R702H mutations were only associated with FTNS, EPS, or APSM, thus defining a region of MYHIIA critical in the combined pathogenesis of macrothrombocytopenia, nephritis, and deafness. The E1841K, D1424N, and R1933X coiled-coil domain mutations were common to both MHA and FTNS. Haplotype analysis using three novel microsatellite markers revealed that three E1841K carriers--one with MHA and two with FTNS--shared a common haplotype around the MYH9 gene, suggesting a common ancestor. The two new globular-head mutations, K371N and R702H, as well as the recently identified MYH9 mutation, R705H, which results in DFNA17, were modeled on the basis of X-ray crystallographic data. Altogether, our data suggest that MHA, SBS, FTNS, EPS, and APSM comprise a phenotypic spectrum of disorders, all caused by MYH9 mutations. On the basis of our genetic analyses, the name "MYHIIA syndrome" is proposed to encompass all of these disorders.
Figures


References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for the human genetic map)
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for human MYH9 [accession number 3135984], Hs MYHIIA [accession number P35579], Rn MYHA [accession number AAA74950], Rn neur MHC [accession number S21801], Gg MYHIIA [AAA48974], Xl MYHIIA [accession number AAC83556], Hs MYHIIB [accession number AAA99177], Rn MYHB [accession number AAF61445], Bt MYHB [accession number BAA36494], Gg MYHIIB [accession number AAA48988], Xl MYHB [accession number AAA49915], Gg SMMHC [accession number P10587], Oc SM2 [accession number P35748], Mm SM2 [accession number JC5421], Dm NMII [accession number AAB09049], and Ce NMYII [accession number AAA83339])
-
- Genome Database, The, http://gdbwww.gdb.org/ (for microsatellite accession numbers)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for MHA [MIM 155100], FTNS [MIM 153640], SBS [MIM 605249], and EPS and APSM [MIM 153650])
-
- Tandem Repeats Finder, http://c3.biomath.mssm.edu/trf.html
References
-
- Atkin CL, Gregory MC, Border WA (1986) Alport syndrome. In: Schrier RW, Gottschalk CW (eds) Strauss and Welt’s diseases of the kidney. Little Brown, Boston, pp 617–641
-
- Avraham KB, Hasson T, Steel KP, Kingsley DM, Russell LB, Mooseker MS, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA (1995) The mouse Snell's waltzer deafness gene encodes an unconventional myosin required for structural integrity of inner ear hair cells. Nat Genet 11:369–375 - PubMed
-
- Bain BJ (1985) Platelet count and platelet size in males and females. Scand J Haematol 35:77–79 - PubMed
-
- Barker DF, Hostikka SL, Zhou J, Chou LT, Oliphant AR, Gerken SC, Gregory MC, Skilnick MH, Atkin CL, Tryggvason K (1990) Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 collagen gene in Alport syndrome. Science 248:1224–1227 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

