The importance of genealogy in determining genetic associations with complex traits
- PMID: 11590549
- PMCID: PMC1274359
- DOI: 10.1086/323659
The importance of genealogy in determining genetic associations with complex traits
Figures
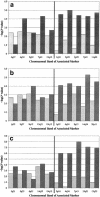
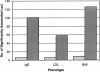
References
-
- Bitti PP, Murgia BS, Ticca A, Ferrai R, Musu L, Piras ML, Puledda E, Campo S, Durando S, Montomoli C, Clayton DG, Mander AP, Bernardinelli L (2001) Association between the ancestral haplotype HLA A30B18DR3 and multiple sclerosis in central Sardinia. Genet Epidemiol 20:271–283 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

