Restoration of atrial mechanical function after successful radio-frequency catheter ablation of atrial flutter
- PMID: 11590904
- PMCID: PMC4531718
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2001.16.2.69
Restoration of atrial mechanical function after successful radio-frequency catheter ablation of atrial flutter
Abstract
Background: Atrial mechanical dysfunction and its recovery time course after successful radiofrequency ablation of chronic atrial flutter (AFL) has been largely unknown. We serially evaluated left atrial function by echocardiography after successful ablation of chronic atrial flutter.
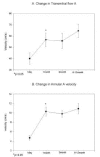
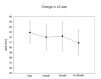
Methods: In 13 patients with chronic AFL, mitral E wave A wave, and the ratio of A/E velocity were measured at 1 day, 1 month, 3 months and 6-12 months after successful radiofrequency (RF) ablation. Doppler tissue imaging (DTI) technique was also used to avoid load-dependent variation in the flow velocity pattern.
Results: Left atrial mechanical function, assessed by A wave velocity and the annular motion, was depressed at 1 day, but improved significantly at 1 month and maintained through 6-12 months after the ablation. Left atrial size did not change significantly.
Conclusion: Left atrial mechanical function was depressed immediately after successful RF ablation of chronic AFL, but it improved significantly after 1 month and was maintained over one year.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Radiofrequency ablation of left atrial flutter mediated with double potentials in a seemingly normally structured heart.Int J Cardiol. 2014 Aug 20;175(3):522-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.06.041. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Int J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25023792
-
Effect of radiofrequency ablation on atrial mechanical function in patients with atrial flutter.Am J Cardiol. 1999 Aug 15;84(4):420-5. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)00348-3. Am J Cardiol. 1999. PMID: 10468080
-
[The effects of the ablation of atrial flutter in patients with and without a clinical history of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation].G Ital Cardiol. 1998 Nov;28(11):1253-60. G Ital Cardiol. 1998. PMID: 9866803 Italian.
-
Factors associated with early atrial fibrillation after ablation of common atrial flutter. A single centre prospective study.Eur Heart J. 2002 Mar;23(6):498-506. doi: 10.1053/euhj.2001.2819. Eur Heart J. 2002. PMID: 11863353
-
Atrial fibrillation inducibility during cavotricuspid isthmus-dependent atrial flutter ablation as a predictor of clinical atrial fibrillation. A meta-analysis.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2017 Apr;48(3):307-315. doi: 10.1007/s10840-016-0211-9. Epub 2017 Jan 9. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28070875 Review.
References
-
- Irani WN, Grayburn PA, Afridi I. Prevalence of thrombus, spontaneous echo contrast and atrial stunning in patients undergoing cardioversion of atrial flutter. A prospective study using transesophageal echocardiography. Circulation. 1997;95:962–966. - PubMed
-
- Woods KA, Eisenberg SJ, Kalman JM, Drew BJ, Saxon LA, Lee RJ, Lesh MD, Scheinman MM. Risk of thromboembolism in chronic atrial flutter. Am J Cardiol. 1997;79:1043–1047. - PubMed
-
- Lanzarotti CJ, Olshansky B. Thromboembolism in chronic atrial flutter: Is the risk underestimated? J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997;30:1506–1511. - PubMed
-
- Schwartzmann D, Callans DJ, Gottlieb CD, Dillon SM, Movsowitz C, Marchlinski FE. Conduction block in the inferior vena caval-tricuspid valve isthmus: association with outcome of radiofrequency ablation of type I atrial flutter. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996;28:1519–1531. - PubMed
-
- Lesh MD, Van Hare GF, Epstein LM, Fitzpatrick AP, Scheinman MM, Lee RJ, Kwasman MA, Grogin HR, Griffin JC. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial arrhythmias. Results and mechanisms. Circulation. 1994;89:1074–1089. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
