Kidney transplantation in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: long-term prognosis for patients and grafts
- PMID: 11590909
- PMCID: PMC4531710
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2001.16.2.98
Kidney transplantation in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: long-term prognosis for patients and grafts
Abstract
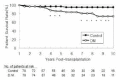
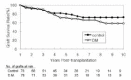
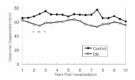
Kidney transplantation is the best therapeutic choice to improve survival and quality of life in patients with end-stage diabetic nephropathy. Long-term prognosis in diabetic patients who received kidney transplants, however, has not been delineated. We, therefore, studied patient and graft survival, graft function and cause of graft failure in 78 Type I diabetic kidney transplant recipients in The Rogosin Institute/The Weill-Cornell Medical Center, New York who had functioning grafts for more than one year. The results were compared with 78 non-diabetic patients who had functioning grafts for more than one year and were matched for age, gender, donor source, time of transplantation and immunosuppressive therapy protocol. Cumulative patient survival rates for diabetic patients were significantly lower than those of non-diabetic patients (86% vs. 97% at 5 years and 74% vs. 95% at 10 years, respectively; p < 0.05). The most common cause of death was cardiovascular disease. Graft survival rates for diabetic patients were also lower than that of non-diabetic patients (71% vs. 80% at 5 years and 58% vs. 72% at 10 years, respectively), but the differences did not reach statistical significance. Among the 22 failed grafts in diabetic patients, 7 (32%) were due to patient death rather than primary graft failure. If the patients who died with a functioning graft were censored, graft survival rates of diabetic patients approached those of non-diabetic patients (80% vs. 81% at 5 years and 65% vs. 73% at 10 years, respectively). Creatinine clearances in diabetic patients were lower than that in non-diabetic patients through the follow-up period, but the differences were significant only for the first few years. At no time was there a higher creatinine clearance for diabetic patients. Among the 16 patients who had transplant kidney biopsies two to seven years post-transplant, 6 showed morphological changes consistent with diabetic nephropathy. One patient lost graft function solely by recurrent diabetic nephropathy. We conclude that long-term patient survival for diabetic patients is significantly lower than that of non-diabetic patients, due primarily to cardiovascular disease. Graft survival is comparable between the two groups. Creatinine clearances of diabetic patients are lower than those of non-diabetic patients. There is no apparent glomerular hyperfiltration at any time in diabetic patients. Recurrence of diabetic nephropathy is a rare cause of graft failure in the first 10 year post-transplant period. Aggressive intervention to modify cardiovascular risk factors should improve patient and graft survival in diabetic kidney transplant recipients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Significance of age in the survival of diabetic patients after kidney transplantation.Int Urol Nephrol. 2002;33(1):173-7. doi: 10.1023/a:1014428817740. Int Urol Nephrol. 2002. PMID: 12090327
-
Long-term survival following kidney transplantation in 100 type I diabetic patients.Transplantation. 1989 Jan;47(1):106-13. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198901000-00024. Transplantation. 1989. PMID: 2643218
-
Does simultaneously transplanted pancreas improve long-term outcome of kidney transplantation in type 1 diabetic recipients?Transplant Proc. 2011 Oct;43(8):3097-101. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2011.08.020. Transplant Proc. 2011. PMID: 21996235
-
Kidney-pancreas transplantation for diabetic nephropathy.Semin Nephrol. 2000 Mar;20(2):188-98. Semin Nephrol. 2000. PMID: 10746860 Review.
-
Pancreas organ transplantation. Short and long-term results in terms of diabetes control.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2000 Oct;385(6):379-89. doi: 10.1007/s004230000124. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2000. PMID: 11127521 Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Absence of Clinically Significant Recurrent Diabetic Kidney Disease on Postmortem Biopsy 32 Years After Kidney Transplantation for Type 1 Diabetes.Transplant Direct. 2021 Nov 17;7(12):e790. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001240. eCollection 2021 Dec. Transplant Direct. 2021. PMID: 34805492 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Influence of diabetes and other risk factors on in-hospital mortality following kidney transplantation: an analysis of the Spanish National Hospital Discharge Database from 2016 to 2020.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2024 Apr 3;12(2):e003799. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2023-003799. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2024. PMID: 38575154 Free PMC article.
-
Access to renal transplantation in the diabetic population-effect of comorbidities and body mass index.Clin Transplant. 2012 May-Jun;26(3):E307-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2012.01661.x. Clin Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22686955 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation in Japanese individuals with type 1 diabetes and end-stage kidney disease.Diabetol Int. 2024 Jan 24;15(2):278-289. doi: 10.1007/s13340-024-00691-z. eCollection 2024 Apr. Diabetol Int. 2024. PMID: 38524933 Free PMC article.
-
Stratification of Kidney Transplant Recipients Into Five Subgroups Based on Temporal Disease Trajectories.Transplant Direct. 2024 Jan 24;10(2):e1576. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001576. eCollection 2024 Feb. Transplant Direct. 2024. PMID: 38274475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Renal Data System USRDS 1998 Annual Data Report. National Institute of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease Bethesda, April 1998.
-
- Goldstein DA, Massry SG. Diabetic nephropathy. Clinical course and effect of hemodialysis. Nephron. 1978;20:286–296. - PubMed
-
- Rosansky SJ. What is the truth about diabetic nephropathy. Diabetic Nephropathy. 2(103):1983.
-
- Port FK, Wolfe RA, Mauger EA, Berline DP, Jiang K. Comparison of survival probabilities for dialysis patients vs cadaveric renal transplant recipients. J Am Med Assoc. 1993;270:1339–1350. - PubMed
-
- Khauli RB, Steinmuller DR, Novick AC, Buszta C, Goormastic M, Nakamoto S, Vidt DG, Magnusson M, Paganini E, Schreiber MJ. A critical look at survival of diabetics with end-stage renal disease. Transplantation. 1986;4:1598–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
