What do patients in a lithium outpatient clinic know about lithium therapy?
- PMID: 11590971
- PMCID: PMC167185
What do patients in a lithium outpatient clinic know about lithium therapy?
Abstract
Objective: To determine how much patients know about lithium therapy and to examine factors that might influence this knowledge.
Setting: Lithium outpatient clinic.
Patients: Patients (n = 123) affiliated with a lithium outpatient clinic (mean treatment duration of 12 years). Diagnoses, according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 3rd edition, revised, included bipolar disorder, recurrent unipolar depression and schizoaffective disorder.
Outcome measures: Quantitative assessment of lithium-related knowledge, obtained by responses to a questionnaire adapted from the Lithium Knowledge Test, and factors affecting this knowledge.
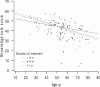
Results: Age was negatively correlated with lithium therapy knowledge scores, whereas duration of treatment, sex, education and diagnosis appeared to be unrelated to knowledge.
Conclusion: Patient education about lithium treatment should be intensified, especially for older patients taking lithium because adverse drug reactions pose a greater risk to the elderly.
Objectif: Déterminer les connaissances des patients à l'égard de la thérapie au lithium et examiner les facteurs susceptibles d'influer sur ces connaissances.
Contexte: Patients traités au lithium en clinique externe.
Patients: Patients (n = 123) affiliés à une clinique externe de traitement au lithium (durée moyenne du traitement : 12 ans). Selon la troisième édition révisée du Manuel diagnostique et statistique des troubles mentaux, les diagnostics comprenaient un trouble bipolaire, une dépression unipolaire récidivante et un trouble schizo-affectif.
Mesures de résultats: Évaluation quantitative des connaissances du traitement par le lithium — obtenue au terme d'un questionnaire adapté du test de connaissance du lithium — et des facteurs influant sur ces connaissances.
Résultats: On a établi une corrélation négative entre l'âge et le résultat obtenu au questionnaire sur la thérapie au lithium, mais aucune corrélation entre la durée du traitement, le sexe, le niveau d'instruction, le diagnostic et le niveau de connaissances.
Conclusion: Il y aurait lieu d'intensifier l'information fournie aux patients sur le traitement au lithium, surtout chez les patients âgés traités au lithium, étant donné les risques plus élevés que posent les réactions défavorables au médicament pour les personnes âgées.
Figures
References
-
- Bowden CL. Key treatment studies of lithium in manic-depressive illness: efficacy and side effects. J Clin Psychiatry 1998; 59(6 Suppl):13-9. - PubMed
-
- Denicoff KD, Smith-Jackson EE, Disney ER, Ali SO, Leverich GS, Post RM. Comparative prophylactic efficacy of lithium, carbamazepine, and the combination in bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 1997;58(11):470-8. - PubMed
-
- Grof P. Has the effectiveness of lithium changed? Impact of the variety of lithium's effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 1998; 19(3):183-8. - PubMed
-
- Greil W, Ludwig-Mayerhofer W, Erazo N, Engel RR, Czernik A, Giedke H, et al. Comparative efficacy of lithium and amitriptyline in the maintenance treatment of recurrent unipolar depression: a randomised study. J Affect Disord 1996;40(3):179-90. - PubMed
-
- Greil W, Ludwig-Mayerhofer W, Erazo N, Schochlin C, Schmidt S, Engel RR, et al. Lithium versus carbamazepine in the maintenance treatment of bipolar disorders — a randomised study. J Affect Disord 1997;43(2):151-61. - PubMed