Accuracy of the Pepin method to determine appropriate lithium dosages in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 11590973
- PMCID: PMC167187
Accuracy of the Pepin method to determine appropriate lithium dosages in healthy volunteers
Abstract
Objective: To assess if the lithium dosage prescribed according to the Pepin method leads to therapeutic serum concentrations of lithium.
Methods: For 13 healthy volunteers, the initial daily doses of lithium were calculated according to the Pepin formula with a view to obtaining a serum lithium level of 0.8 mmol/L. Lithium was administered twice daily for 21 days, and blood samples were drawn daily, 12 hours after the last dose was taken. Dosage was adjusted if serum concentrations were below 0.6 mmol/L or above 1.0 mmol/L or if major side effects were reported.
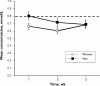
Results: Daily lithium doses ranged from 1050 mg to 1950 mg (mean 1569 mg, standard deviation [SD] 291 mg), The mean serum lithium concentrations for weeks 1, 2 and 3 were 0.74 mmol/L (SD 0.19 mmol/L), 0.67 mmol/L (SD 0.22 mmol/L) and 0.69 mmol/L (SD 0.13 mmol/L), respectively. Within-subject variance was negligible. Sixty-eight percent of the serum lithium concentration measurements fell between 0.57 mmol/L and 0.83 mmol/L, and 84% fell within the recommended therapeutic range of 0.60 mmol/L and 1.20 mmol/L.
Conclusions: The Pepin method is a safe but conservative method for predicting the appropriate daily dose of lithium.
Objectif: Déterminer si la dose de lithium prescrite selon la méthode Pepin produit des concentrations thérapeutiques de lithium dans le sérum.
Méthodes: Chez 13 volontaires en bonne santé, on a calculé les doses quotidiennes initiales de lithium en fonction de la formule Pepin afin d'obtenir des taux de 0,8 mmol/L de lithium dans le sérum. Le lithium a été administré deux fois par jour pendant 21 jours et l'on a prélevé des échantillons de sang tous les jours, 12 heures après la dernière dose. On a rajusté la posologie si les taux sériques tombaient à moins de 0,6 mmol/L ou dépassaient 1,0 mmol/L, ou si l'on signalait des effets secondaires importants.
Résultats: Les doses quotidiennes de lithium ont varié de 1050 mg à 1950 mg (moyenne de 1569 mg, écart type [ET] de 291 mg). Les concentrations moyennes de lithium dans le sérum au cours des semaines 1, 2 et 3 se sont établies à 0,74 mmol/L (ET, 0,19 mmol/L), 0,67 mmol/L (ET, 0,22 mmol/L) et 0,69 mmol/L (ET, 0,13 mmol/L) respectivement. L'écart chez un même sujet a été négligeable. Soixante-huit pour cent des mesures de concentration du lithium dans le sérum ont varié de 0,57 mmol/L à 0,83 mmol/L et 84 % se sont établies à l'intérieur de la plage thérapeutique recommandée de 0,60 mmol/L à 1,20 mmol/L.
Conclusions: La méthode Pepin est une façon sécuritaire mais conservatrice de calculer la bonne dose quotidienne de lithium.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry 1994;151(Suppl 12):1-36. - PubMed
-
- Sharma V, Yatham L, Haslam D, Silverstone P, Parikh S, Matte R, et al. Continuation and prohylactic treatment of bipolar disorder. Can J Psychiatry 1997;42(Suppl 2):92S-100S. - PubMed
-
- Peterse JW, Havenaar J, Van Rijn H. Possible hazard in use of priming dose to determine lithium dosage. Am J Psychiatry 1999;156(1):157-8. - PubMed
-
- Cooper TB, Simpson GM. The 24 hour lithium level as a progosticator of dosage requirements. Am J Psychiatry 1976;133: 440-3. - PubMed
-
- Perry PJ, Prince RA, Alexander B, Dunner FJ. Prediction of lithium maintenance doses using a single point prediction protocol. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1983;3(1):13-7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical