Molecular cloning and functional analysis of the MutY homolog of Deinococcus radiodurans
- PMID: 11591657
- PMCID: PMC100089
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.21.6151-6158.2001
Molecular cloning and functional analysis of the MutY homolog of Deinococcus radiodurans
Abstract
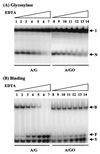
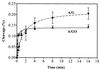
The mutY homolog gene (mutY(Dr)) from Deinococcus radiodurans encodes a 39.4-kDa protein consisting of 363 amino acids that displays 35% identity to the Escherichia coli MutY (MutY(Ec)) protein. Expressed MutY(Dr) is able to complement E. coli mutY mutants but not mutM mutants to reduce the mutation frequency. The glycosylase and binding activities of MutY(Dr) with an A/G-containing substrate are more sensitive to high salt and EDTA concentrations than the activities with an A/7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (GO)-containing substrate are. Like the MutY(Ec) protein, purified recombinant MutY(Dr) expressed in E. coli has adenine glycosylase activity with A/G, A/C, and A/GO mismatches and weak guanine glycosylase activity with a G/GO mismatch. However, MutY(Dr) exhibits limited apurinic/apyrimidinic lyase activity and can form only weak covalent protein-DNA complexes in the presence of sodium borohydride. This may be due to an arginine residue that is present in MutY(Dr) at the position corresponding to the position of MutY(Ec) Lys142, which forms the Schiff base with DNA. The kinetic parameters of MutY(Dr) are similar to those of MutY(Ec). Although MutY(Dr) has similar substrate specificity and a binding preference for an A/GO mismatch over an A/G mismatch, as MutY(Ec) does, the binding affinities for both mismatches are slightly lower for MutY(Dr) than for MutY(Ec). Thus, MutY(Dr) can protect the cell from GO mutational effects caused by ionizing radiation and oxidative stress.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Enhanced activity of adenine-DNA glycosylase (Myh) by apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease (Ape1) in mammalian base excision repair of an A/GO mismatch.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Feb 1;29(3):743-52. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.3.743. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11160897 Free PMC article.
-
Adenine excisional repair function of MYH protein on the adenine:8-hydroxyguanine base pair in double-stranded DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Dec 15;28(24):4912-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.24.4912. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. PMID: 11121482 Free PMC article.
-
Potential double-flipping mechanism by E. coli MutY.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;68:349-64. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(01)68111-x. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11554310 Review.
-
A single engineered point mutation in the adenine glycosylase MutY confers bifunctional glycosylase/AP lyase activity.Biochemistry. 2000 Aug 22;39(33):10098-109. doi: 10.1021/bi0004652. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10955998
-
Multiple DNA glycosylases for repair of 8-oxoguanine and their potential in vivo functions.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;68:193-205. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(01)68100-5. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11554297 Review.
Cited by
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis mutY is involved in the repair of oxidative stress-induced DNA mispairing.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2011 Jun;26(3):175-86. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2011.00605.x. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21545695 Free PMC article.
-
A Decade of Biochemical and Structural Studies of the DNA Repair Machinery of Deinococcus radiodurans: Major Findings, Functional and Mechanistic Insight and Challenges.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2016 Apr 7;14:168-176. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2016.04.001. eCollection 2016. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2016. PMID: 27924191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimutator role of DNA glycosylase MutY in pathogenic Neisseria species.J Bacteriol. 2005 Apr;187(8):2801-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.8.2801-2809.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15805527 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011 Mar;75(1):133-91. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00015-10. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21372322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of a MutY DNA glycosylase in combating oxidative DNA damage in Helicobacter pylori.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Jan 4;6(1):19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.08.006. Epub 2006 Sep 25. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 16996809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Battista J R. Against all odds: the survival strategies of Deinococcus radiodurans. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1997;51:203–224. - PubMed
-
- Battista J R, Earl A M, Park M J. Why is Deinococcus radiodurans so resistant to ionizing radiation? Trends Microbiol. 1999;7:362–365. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

