Comparison of mechanisms of action of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) antagonist cetrorelix and LHRH agonist triptorelin on the gene expression of pituitary LHRH receptors in rats
- PMID: 11593037
- PMCID: PMC59791
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.211442598
Comparison of mechanisms of action of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) antagonist cetrorelix and LHRH agonist triptorelin on the gene expression of pituitary LHRH receptors in rats
Abstract
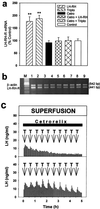
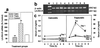
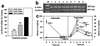
The mechanisms through which luteinizing hormone (LH)-releasing hormone (LHRH) antagonists suppress pituitary gonadotroph functions and LHRH-receptor (LHRH-R) expression are incompletely understood. Consequently, we investigated the direct effect of LHRH antagonist cetrorelix in vitro on the expression of the pituitary LHRH-R gene and its ability to counteract the exogenous LHRH and the agonist triptorelin in the regulation of this gene. We also compared the effects of chronic administration of cetrorelix and triptorelin on the LHRH-R mRNA level and gonadotropin secretion in ovariectomized (OVX) and normal female rats. The exposure of pituitary cells in vitro to 3-min pulses of 1 nM LHRH or 0.1 nM triptorelin for 5 h increased the LHRH-R mRNA level by 77-88%. Continuous perfusion of the cells with 50 nM cetrorelix did not cause any significant changes, but prevented the stimulatory effect of LHRH pulses on the receptor mRNA expression. In OVX rats, 10 days after administration of a depot formulation of cetrorelix, releasing 100 microg of peptide daily, the elevated LHRH-R mRNA level was decreased by 73%, whereas daily injection of 100 microg of triptorelin caused a 41% suppression. In normal female rats, cetrorelix treatment suppressed the LHRH-R mRNA level by 33%, but triptorelin increased it by 150%. The highly elevated serum LH levels in OVX rats and the normal LH concentration of cycling rats were rapidly and completely suppressed by cetrorelix. Triptorelin decreased the serum LH in OVX rats to the precastration level, but had no effect on basal LH in normal rats. Our results confirm that LHRH antagonists, such as cetrorelix, inhibit the gene expression of pituitary LHRH-R indirectly, by counteracting the stimulatory effect of LHRH. A rapid suppression of serum LH by LHRH antagonists would be advantageous in the treatment of sex hormone-dependent tumors and other conditions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of long-term treatment with the luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonist Decapeptyl and the LHRH antagonist Cetrorelix on the levels of pituitary LHRH receptors and their mRNA expression in rats.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Nov 12;99(23):15048-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.232579499. Epub 2002 Oct 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12409615 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic administration of the luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) antagonist cetrorelix decreases gonadotrope responsiveness and pituitary LHRH receptor messenger ribonucleic acid levels in rats.Endocrinology. 1996 Aug;137(8):3430-6. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.8.8754771. Endocrinology. 1996. PMID: 8754771
-
Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LH-RH) antagonist Cetrorelix down-regulates the mRNA expression of pituitary receptors for LH-RH by counteracting the stimulatory effect of endogenous LH-RH.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 13;98(4):1829-34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.98.4.1829. Epub 2001 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11172036 Free PMC article.
-
Role of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) in ovarian cancer.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2003 Oct 7;1:65. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-1-65. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 14594454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparisons of the potential utility of LHRH agonists and antagonists for fertility control.J Steroid Biochem. 1985 Nov;23(5B):779-91. doi: 10.1016/s0022-4731(85)80014-5. J Steroid Biochem. 1985. PMID: 3001420 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of long-term treatment with low doses of the LHRH antagonist Cetrorelix on pituitary receptors for LHRH and gonadal axis in male and female rats.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Apr 6;101(14):4996-5001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400605101. Epub 2004 Mar 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15044692 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Immunotherapy with LHRH-R Targeted Lytic Peptide in Ovarian Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2020 Nov;19(11):2396-2406. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0030. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Mol Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32943548 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of bovine adrenocortical cells encapsulated in alginate.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 24;112(8):2527-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1500242112. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25675525 Free PMC article.
-
Folliculogenesis Is Not Fully Inhibited during GnRH Analogues Treatment in Mice Challenging Their Efficiency to Preserve the Ovarian Reserve during Chemotherapy in This Model.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 1;10(9):e0137164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137164. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26325271 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of GnRH I receptor gene expression by the GnRH agonist triptorelin, estradiol, and progesterone in the gonadotroph-derived cell line alphaT3-1.Endocrine. 2006 Aug;30(1):139-44. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:30:1:139. Endocrine. 2006. PMID: 17185802
References
-
- Schally A V, Comaru-Schally A M, Nagy A, Kovacs M, Szepeshazi K, Plonowski A, Varga J, Halmos G. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2001;22:1–44. - PubMed
-
- Schally A V, Halmos G, Rekasi Z, Arencibia J M. In: Clinic: Infertility and Reproductive Medicine Clinics of North America-January 2001. Devroey P, editor. Vol. 12. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2001. pp. 17–44.
-
- Conn P M. Endocr Rev. 1986;7:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Gordon K, Hodgen G D. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1992;7:259–263. - PubMed
-
- Clayton R N, Catt K J. Endocr Rev. 1981;2:186–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

