Exploration of the pore structure of a peptide-gated Na+ channel
- PMID: 11598003
- PMCID: PMC125683
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.20.5595
Exploration of the pore structure of a peptide-gated Na+ channel
Abstract
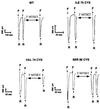
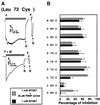
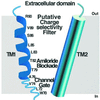
The FMRF-amide-activated sodium channel (FaNaC), a member of the ENaC/Degenerin family, is a homotetramer, each subunit containing two transmembrane segments. We changed independently every residue of the first transmembrane segment (TM1) into a cysteine and tested each position's accessibility to the cysteine covalent reagents MTSET and MTSES. Eleven mutants were accessible to the cationic MTSET, showing that TM1 faces the ion translocation pathway. This was confirmed by the accessibility of cysteines present in the acid-sensing ion channels and other mutations introduced in FaNaC TM1. Modification of accessibilities for positions 69, 71 and 72 in the open state shows that the gating mechanism consists of the opening of a constriction close to the intracellular side. The anionic MTSES did not penetrate into the channel, indicating the presence of a charge selectivity filter in the outer vestibule. Furthermore, amiloride inhibition resulted in the channel occlusion in the middle of the pore. Summarizing, the ionic pore of FaNaC includes a large aqueous cavity, with a charge selectivity filter in the outer vestibule and the gate close to the interior.
Figures
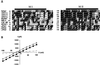



References
-
- Akabas M.H., Stauffer,D.A., Xu,M. and Karlin,A. (1992) Acetylcholine receptor channel structure probed in cysteine-substitution mutants. Science, 258, 307–310. - PubMed
-
- Askwith C.C., Cheng,C., Ikuma,M., Benson,C., Price,M.P. and Welsh,M.J. (2000) Neuropeptide FF and FMRF-amide potentiate acid-evoked currents from sensory neurons and proton-gated DEG/ENaC channels. Neuron, 26, 133–141. - PubMed
-
- Benson C.J., Eckert,S.P. and McCleskey,E.W. (1999) Acid-evoked currents in cardiac sensory neurons: A possible mediator of myocardial ischemic sensation. Circ. Res., 84, 921–928. - PubMed
-
- Canessa C.M., Merillat,A.M. and Rossier,B.C. (1994) Membrane topology of the epithelial sodium channel in intact cells. Am. J. Physiol., 267, C1682–C1690. - PubMed
-
- Chalfie M.and Wolinski,E. (1990) The identification and suppression of inherited neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature, 345, 410–416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

