Relative importance of NF-kappaB p50 in mycobacterial infection
- PMID: 11598086
- PMCID: PMC100095
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.11.7100-7105.2001
Relative importance of NF-kappaB p50 in mycobacterial infection
Abstract
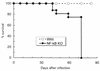
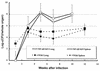
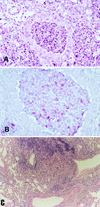
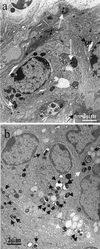
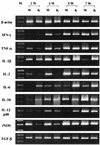
To understand the role of NF-kappaB in the development of murine tuberculosis in vivo, NF-kappaB p50 knockout mice were infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis by placing them in the exposure chamber of an airborne-infection apparatus. These mice developed multifocal necrotic pulmonary lesions or lobar pneumonia. Compared with the levels in wild-type mice, pulmonary inducible nitric oxide synthase, interleukin-2 (IL-2), gamma interferon, and tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA levels were significantly low but expression of IL-10 and transforming growth factor beta mRNAs were within the normal ranges. The pulmonary IL-6 mRNA expression level was higher. Therefore, NF-kappaB and its interaction with host cells play an important role in the pathogenesis of tuberculosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferon regulatory factor 1 in mycobacterial infection.Microbiol Immunol. 2002;46(11):751-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2002.tb02760.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12516771
-
Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in Mycobacterium-induced granuloma formation in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-deficient mice.Lab Invest. 1999 Apr;79(4):379-86. Lab Invest. 1999. PMID: 10211990
-
Disruption of nuclear factor-interleukin-6, a transcription factor, results in severe mycobacterial infection.Am J Pathol. 2001 Feb;158(2):361-6. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63977-6. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11159172 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterial infection in TLR2 and TLR6 knockout mice.Microbiol Immunol. 2003;47(5):327-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2003.tb03404.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12825894
-
Effects of NF-kappaB1 (p50) targeted gene disruption on ionizing radiation-induced NF-kappaB activation and TNFalpha, IL-1alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 mRNA expression in vivo.Int J Radiat Biol. 2001 Jul;77(7):763-72. doi: 10.1080/09553000110050047. Int J Radiat Biol. 2001. PMID: 11454276
Cited by
-
Transcription factor MAFB controls type I and II interferon response-mediated host immunity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 3;13:962306. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.962306. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36406405 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction pathways of tumor necrosis factor--mediated lung injury induced by ozone in mice.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007 Apr 15;175(8):829-39. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200509-1527OC. Epub 2007 Jan 25. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007. PMID: 17255564 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological and immunological profiles of rat tuberculosis.Int J Exp Pathol. 2004 Jun;85(3):125-34. doi: 10.1111/j.0959-9673.2004.00379.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15255966 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Screening System of Virulent Strains for the Establishment of a Mycobacterium avium Complex Lung Disease Mouse Model Using Whole-Genome Sequencing.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0045122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00451-22. Epub 2022 May 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35579455 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage polarization drives granuloma outcome during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.Infect Immun. 2015 Jan;83(1):324-38. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02494-14. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25368116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bacuerle P, Henkel T. Function and activation of NK-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
-
- Bernier R, Barbeau B, Olivier M, Tremblay M J. Mycobacterium tuberculosis mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan can induce NK-kappa B-dependent activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat in T cells. J Gen Virol. 1998;79:1353–1361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

