A 4.1-kilodalton polypeptide in the cultural supernatant of Mycoplasma fermentans is one of the substances responsible for induction of interleukin-6 production by human gingival fibroblasts
- PMID: 11598097
- PMCID: PMC100118
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.11.7173-7177.2001
A 4.1-kilodalton polypeptide in the cultural supernatant of Mycoplasma fermentans is one of the substances responsible for induction of interleukin-6 production by human gingival fibroblasts
Abstract
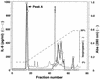
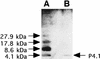
The cultural supernatant of Mycoplasma fermentans induced interleukin-6 production by human gingival fibroblasts. The active entities were divided into hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances. In this study, we purified a 4.1-kilodalton polypeptide from the hydrophilic substances. It reacted with polyclonal antibodies to M. fermentans and activated human macrophages.
Figures


References
-
- Chingbingyong M I, Hughes C V. Detection of Mycoplasma fermentans in human saliva with a polymerase chain reaction based assay. Arch Oral Biol. 1996;41:311–314. - PubMed
-
- Dong L, Shibata K-I, Sawa Y, Hasebe A, Yamaoka Y, Yoshida S, Watanabe T. Transcriptional activation of mRNA of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and induction of its cell surface expression in normal human gingival fibroblasts by Mycoplasma salivarium and Mycoplasma fermentans. Infect Immun. 1999;67:3061–3065. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dully J R, Grieve P A. A simple technique for eliminating interference by detergents in the Lowry method of protein determination. Anal Biochem. 1975;64:136–141. - PubMed
-
- Fox J D, Robyt J F. Miniaturization of three carbohydrate analyses using a microsample plate reader. Anal Biochem. 1991;195:93–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

