Dual role of H-Ras in regulation of lymphocyte function antigen-1 activity by stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha: implications for leukocyte transmigration
- PMID: 11598192
- PMCID: PMC60156
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.10.3074
Dual role of H-Ras in regulation of lymphocyte function antigen-1 activity by stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha: implications for leukocyte transmigration
Abstract
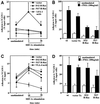
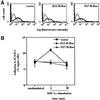
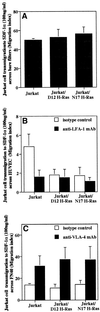
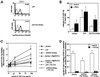
We investigated the role of H-Ras in chemokine-induced integrin regulation in leukocytes. Stimulation of Jurkat T cells with the CXC chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha (SDF-1alpha) resulted in a rapid increase in the phosphorylation, i.e., activation of extracellular signal receptor-activated kinase (ERK) but not c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase or p38 kinase, and phosphorylation of Akt, reflecting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K) activation. Phosphorylation of ERK in Jurkat cells was enhanced and attenuated by expression of dominant active (D12) or inactive (N17) forms of H-Ras, respectively, while N17 H-Ras abrogated SDF-1alpha-induced Akt phosphorylation. SDF-1alpha triggered a transient regulation of adhesion to intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 mediated by lymphocyte function antigen-1 (LFA-1) and very late antigen-4 (VLA-4), respectively, and a rapid increase in LFA-1 binding to soluble ICAM-1.Ig, which was inhibited by D12 but not N17 H-Ras. Both D12 and N17 H-Ras abrogated the regulation of LFA-1 but not VLA-4 avidity, and impaired LFA-1-mediated transendothelial chemotaxis but not VLA-4-dependent transmigration induced by SDF-1alpha. Analysis of the mutant Jurkat J19 clone revealed LFA-1 with constitutively high affinity and reduced ERK phosphorylation, which were partially restored by expression of active H-Ras. Inhibition of PI3-K blocked the up-regulation of Jurkat cell adhesion to ICAM-1 by SDF-1alpha, whereas inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase impaired the subsequent down-regulation and blocking both pathways abrogated LFA-1 regulation. Our data suggest that inhibition of initial PI3-K activation by inactive H-Ras or sustained activation of an inhibitory ERK pathway by active H-Ras prevail to abolish LFA-1 regulation and transendothelial migration induced by SDF-1alpha in leukocytes, establishing a complex and bimodal involvement of H-Ras.
Figures




References
-
- Baggiolini M. Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature. 1998;392:565–568. - PubMed
-
- Campbell JJ, Hedrick J, Zlotnik A, Siani MA, Thompson DA, Butcher EC. Chemokines and the arrest of lymphocytes rolling under flow conditions. Science. 1998;279:381–384. - PubMed
-
- Capodici C, Hanft S, Feoktistov M, Pillinger MH. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mediates chemoattractant-stimulated, CD11b/CD18-dependent cell-cell adhesion of human neutrophils: evidence for an ERK-independent pathway. J Immunol. 1998;160:1901–1909. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary A, King WG, Mattaliano MD, Frost JA, Diaz B, Morrison DK, Cobb MH, Marshall MS, Brugge JS. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulates Raf1 through Pak phosphorylation of serine 338. Curr Biol. 2000;10:551–554. - PubMed
-
- Clark EA, Brugge JS. Integrins and signal transduction pathways: the road taken. Science. 1995;268:233–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

