Control of specific gene expression by gibberellin and brassinosteroid
- PMID: 11598220
- PMCID: PMC125081
Control of specific gene expression by gibberellin and brassinosteroid
Abstract
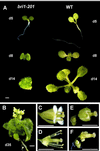
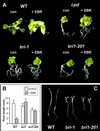
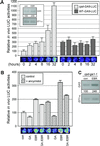
We identified a recessive, brassinolide-insensitive mutant caused by a deletion allele (bri1-201) of the brassinosteroid (BR) receptor BRI1. The bri1-201 mutant displayed altered expression levels of genes differentially regulated by gibberellin (GA). RNA-blot analysis revealed that BR and GA antagonistically regulate the accumulation of mRNAs of the GA-responsive GASA1 gene, as well as the GA-repressible GA5 gene. Expression studies with cycloheximide indicated that the antagonistic effects of GA and BR on GA5 require de novo protein synthesis. Reporter transgene analyses and RNA-blot analysis showed that BR and GA modulate GA5 expression, at least in part, at the transcriptional level, and that the signals are independent and subtractive.
Figures


References
-
- Axelos M, Bardet C, Liboz T, Le Van Thai A, Curie C, Lescure B. The gene family encoding the Arabidopsis thaliana translation elongation factor EF-1 alpha: molecular cloning, characterization and expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1989;219:106–112. - PubMed
-
- Bell CJ, Ecker JR. Assignment of 30 microsatellite loci to the linkage map of Arabidopsis. Genomics. 1994;19:137–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
