Biochemical and genetic analysis of the effects of amylose-extender mutation in rice endosperm
- PMID: 11598221
- PMCID: PMC125082
Biochemical and genetic analysis of the effects of amylose-extender mutation in rice endosperm
Abstract
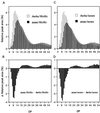
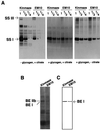
Biochemical analysis of amylose-extender (ae) mutant of rice (Oryza sativa) revealed that the mutation in the gene for starch-branching enzyme IIb (BEIIb) specifically altered the structure of amylopectin in the endosperm by reducing short chains with degree of polymerization of 17 or less, with the greatest decrease in chains with degree of polymerization of 8 to 12. The extent of such change was correlated with the gelatinization properties of the starch granules, as determined in terms of solubility in urea solution. The ae mutation caused a dramatic reduction in the activity of BEIIb. The activity of soluble starch synthase I (SSI) in the ae mutant was significantly lower than in the wild type, suggesting that the mutation had a pleiotropic effect on the SSI activity. In contrast, the activities of BEI, BEIIa, ADP-Glc pyrophosphorylase, isoamylase, isoamylase, pullulanase, and Suc synthase were not affected by the mutation. Therefore, it is stressed that the function of BEIIb cannot be complemented by BEIIa and BEI. These results strongly suggest that BEIIb plays a specific role in the transfer of short chains, which might then be extended by SS to form the A and B(1) chains of amylopectin cluster in rice endosperm.
Figures



References
-
- Abel GJW, Springer F, Willmitzer L, Kossmann J. Cloning and functional analysis of a cDNA encoding a novel 139 kDa starch synthase from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Plant J. 1996;10:981–991. - PubMed
-
- Adkins GK, Greenwood CT, Hourston DJ. Studies on starches of high amylose content: XI. Some physicochemical properties of dispersions of amylomaize starch, and observations on the nature of high-amylose starches. Cereal Chem. 1970;47:13–18.
-
- Baba T, Arai Y. Structural characterization of amylopectin and intermediate material in amylomaize starch granules. Agric Biol Chem. 1984;48:1763–1775.
-
- Baba T, Kim S-J, Arai Y. Treatment of amylomaize starch granules with urea: comparison with normal maize starch. Carbohydr Res. 1983;124:344–348.
-
- Banks W, Greenwood CT, Muir DD. Studies on starches of high amylose content: part 17. A review of current concepts. Starch. 1974;26:289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
