Arabidopsis and the heat stress transcription factor world: how many heat stress transcription factors do we need?
- PMID: 11599559
- PMCID: PMC434399
- DOI: 10.1379/1466-1268(2001)006<0177:aathst>2.0.co;2
Arabidopsis and the heat stress transcription factor world: how many heat stress transcription factors do we need?
Abstract
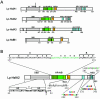
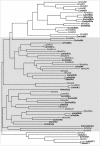
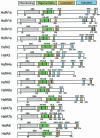
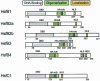
Sequencing of the Arabidopsis genome revealed a unique complexity of the plant heat stress transcription factor (Hsf) family. By structural characteristics and phylogenetic comparison, the 21 representatives are assigned to 3 classes and 14 groups. Particularly striking is the finding of a new class of Hsfs (AtHsfC1) closely related to Hsf1 from rice and to Hsfs identified from frequently found expressed sequence tags of tomato, potato, barley, and soybean. Evidently, this new type of Hsf is well expressed in different plant tissues. Besides the DNA binding and oligomerization domains (HR-A/B region), we identified other functional modules of Arabidopsis Hsfs by sequence comparison with the well-characterized tomato Hsfs. These are putative motifs for nuclear import and export and transcriptional activation (AHA motifs). There is intriguing flexibility of size and sequence in certain parts of the otherwise strongly conserved N-terminal half of these Hsfs. We have speculated about possible exon-intron borders in this region in the ancient precursor gene of plant Hsfs, similar to the exon-intron structure of the present mammalian Hsf-encoding genes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of C-terminal domains of Arabidopsis heat stress transcription factors (Hsfs) and identification of a new signature combination of plant class A Hsfs with AHA and NES motifs essential for activator function and intracellular localization.Plant J. 2004 Jul;39(1):98-112. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02111.x. Plant J. 2004. PMID: 15200645
-
Arabidopsis HsfB1 and HsfB2b act as repressors of the expression of heat-inducible Hsfs but positively regulate the acquired thermotolerance.Plant Physiol. 2011 Nov;157(3):1243-54. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.179036. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21908690 Free PMC article.
-
Tomato heat stress transcription factor HsfB1 represents a novel type of general transcription coactivator with a histone-like motif interacting with the plant CREB binding protein ortholog HAC1.Plant Cell. 2004 Jun;16(6):1521-35. doi: 10.1105/tpc.019927. Epub 2004 May 6. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15131252 Free PMC article.
-
Heat stress response in plants: a complex game with chaperones and more than twenty heat stress transcription factors.J Biosci. 2004 Dec;29(4):471-87. doi: 10.1007/BF02712120. J Biosci. 2004. PMID: 15625403 Review.
-
The plant heat stress transcription factor (Hsf) family: structure, function and evolution.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Feb;1819(2):104-19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.10.002. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22033015 Review.
Cited by
-
Common and distinct functions of Arabidopsis class A1 and A2 heat shock factors in diverse abiotic stress responses and development.Plant Physiol. 2013 Sep;163(1):276-90. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.221168. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23832625 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Genetic Diversity in Adzuki Beans (Vigna angularis): Insights into Environmental Adaptation and Early Breeding Strategies for Yield Improvement.Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 13;12(24):4154. doi: 10.3390/plants12244154. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38140482 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of HSF Gene Family in Kiwifruit and the Function of AeHSFA2b in Salt Tolerance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 27;24(21):15638. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115638. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958622 Free PMC article.
-
The Heat Stress Factor HSFA6b Connects ABA Signaling and ABA-Mediated Heat Responses.Plant Physiol. 2016 Oct;172(2):1182-1199. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00860. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27493213 Free PMC article.
-
HEAT SHOCK FACTOR A8a Modulates Flavonoid Synthesis and Drought Tolerance.Plant Physiol. 2020 Nov;184(3):1273-1290. doi: 10.1104/pp.20.01106. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Plant Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32958560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aranda MA, Escaler M, Thomas CL, Maule AJ. A heat stress transcription factor in pea is differentially controlled by heat and virus replication. Plant J. 1999;20:153–161. - PubMed
-
- Bharti K, Schmidt E, Lyck R, Bublak D, Scharf KD. Isolation and characterization of HsfA3, a new heat stress transcription factor of Lycopersicon peruvianum. Plant J. 2000;22:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Bienz M, Pelham HRB. Mechanisms of heat-shock gene activation in higher eukaryotes. Adv Genet. 1987;24:31–72. - PubMed
-
- Clos J, Westwood JT, Becker PB, Wilson S, Lambert U, Wu C. Molecular cloning and expression of a heaxameric Drosophila heat stress factor subject to negative regulation. Cell. 1990;63:1085–1097. - PubMed
-
- Czarnecka-Verner E, Yuan CX, Fox PC, Gurley WB. Isolation and characterization of six heat stress transcription factor cDNA clones from soybean. Plant Mol Biol. 1995;29:37–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
