Irresistible IRES. Attracting the translation machinery to internal ribosome entry sites
- PMID: 11600453
- PMCID: PMC1084086
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kve208
Irresistible IRES. Attracting the translation machinery to internal ribosome entry sites
Abstract
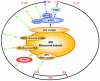
Studies on the control of eukaryotic translation initiation by a cap-independent recruitment of the 40S ribosomal subunit to internal messenger RNA sequences called internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) have shown that these sequence elements are present in a growing list of viral and cellular RNAs. Here we discuss their prevalence, mechanisms whereby they may function and their uses in regulating gene expression.
Figures
References
-
- Bonneau A.M. and Sonenberg, N. (1987) Involvement of the 24-kDa cap-binding protein in regulation of protein synthesis in mitosis. J. Biol. Chem., 262, 11134–11139. - PubMed
-
- Chappell S.A., LeQuesne, J.P., Paulin, F.E., deSchoolmeester, M.L., Stoneley, M., Soutar, R.L., Ralston, S.H., Helfrich, M.H. and Willis, A.E. (2000b) A mutation in the c-myc-IRES leads to enhanced internal ribosome entry in multiple myeloma: a novel mechanism of oncogene de-regulation. Oncogene, 19, 4437–4440. - PubMed
-
- Coldwell M.J., Mitchell, S.A., Stoneley, M., MacFarlane, M. and Willis, A.E. (2000) Initiation of Apaf-1 translation by internal ribosome entry. Oncogene, 19, 899–905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

