Muscle-derived interleukin-6: possible biological effects
- PMID: 11600669
- PMCID: PMC2278876
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0329c.xd
Muscle-derived interleukin-6: possible biological effects
Abstract
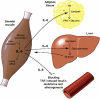
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is produced locally in working skeletal muscle and can account for the increase in plasma IL-6 during exercise. The production of IL-6 during exercise is related to the intensity and duration of the exercise, and low muscle glycogen content stimulates the production. Muscle-derived IL-6 is released into the circulation during exercise in high amounts and is likely to work in a hormone-like fashion, exerting an effect on the liver and adipose tissue, thereby contributing to the maintenance of glucose homeostasis during exercise and mediating exercise-induced lipolysis. Muscle-derived IL-6 may also work to inhibit the effects of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor alpha. The latter cytokine is produced by adipose tissue and inflammatory cells and appears to play a pathogenetic role in insulin resistance and atherogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Muscle-derived interleukin-6: lipolytic, anti-inflammatory and immune regulatory effects.Pflugers Arch. 2003 Apr;446(1):9-16. doi: 10.1007/s00424-002-0981-z. Epub 2003 Feb 18. Pflugers Arch. 2003. PMID: 12690457 Review.
-
Muscle-derived interleukin-6--a possible link between skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, liver, and brain.Brain Behav Immun. 2005 Sep;19(5):371-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2005.04.008. Brain Behav Immun. 2005. PMID: 15935612
-
The metabolic role of IL-6 produced during exercise: is IL-6 an exercise factor?Proc Nutr Soc. 2004 May;63(2):263-7. doi: 10.1079/PNS2004338. Proc Nutr Soc. 2004. PMID: 15294041 Review.
-
Control of gluconeogenic genes during intense/prolonged exercise: hormone-independent effect of muscle-derived IL-6 on hepatic tissue and PEPCK mRNA.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009 Dec;107(6):1830-9. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00739.2009. Epub 2009 Oct 22. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009. PMID: 19850730
-
Exhaustive exercise causes an anti-inflammatory effect in skeletal muscle and a pro-inflammatory effect in adipose tissue in rats.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2009 Jul;106(5):697-704. doi: 10.1007/s00421-009-1070-1. Epub 2009 May 8. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19424714
Cited by
-
Branched-Chain Amino Acids Supplementation Does Not Accelerate Recovery after a Change of Direction Sprinting Exercise Protocol.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 16;14(20):4331. doi: 10.3390/nu14204331. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36297014 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Acute interleukin-6 administration does not impair muscle glucose uptake or whole-body glucose disposal in healthy humans.J Physiol. 2003 Apr 15;548(Pt 2):631-8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.032938. Epub 2003 Mar 14. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12640021 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
CRISPR-delivery particles targeting nuclear receptor-interacting protein 1 (Nrip1) in adipose cells to enhance energy expenditure.J Biol Chem. 2018 Nov 2;293(44):17291-17305. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004554. Epub 2018 Sep 6. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30190322 Free PMC article.
-
Searching for the exercise factor: is IL-6 a candidate?J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2003;24(2-3):113-9. doi: 10.1023/a:1026070911202. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2003. PMID: 14609022 Review.
-
The Effects of Acute and Chronic Sprint-Interval Training on Cytokine Responses Are Independent of Prior Caffeine Intake.Front Physiol. 2018 Jun 5;9:671. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00671. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29922173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Taga T, Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 in biology and medicine. Advances in Immunology. 1993;54:1–78. - PubMed
-
- Austin L, Bower J, Kurek J, Vakakis N. Effects of leukaemia inhibitory factor and other cytokines on murine and human myoblast proliferation. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 1992;112:185–191. - PubMed
-
- Austin L, Burgess AW. Stimulation of myoblast proliferation in culture by leukaemia inhibitory factor and other cytokines. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 1991;101:193–197. - PubMed
-
- Bartoccioni E, Michaelis D, Hohlfeld R. Constitutive and cytokine-induced production of interleukin-6 by human myoblasts. Immunology Letters. 1994;42:135–138. - PubMed
-
- Bruunsgaard H, Andersen-Ranberg K, Jeune B, Pedersen AN, Skinhoj P, Pedersen B K. A high plasma concentration of TNF-alpha is associated with dementia in centenarians. Journals of Gerontology. 1999;54A:357–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources