Developmental changes in P2X purinoceptors on glycinergic presynaptic nerve terminals projecting to rat substantia gelatinosa neurones
- PMID: 11600685
- PMCID: PMC2278888
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0505c.xd
Developmental changes in P2X purinoceptors on glycinergic presynaptic nerve terminals projecting to rat substantia gelatinosa neurones
Abstract
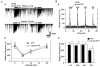
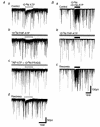
1. In mechanically dissociated rat spinal cord substantia gelatinosa (SG) neurones attached with native presynaptic nerve endings, glycinergic miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) were recorded using nystatin perforated patch recording mode under voltage-clamp conditions. Under these conditions, it was tested whether the changes in P2X receptor subtype on the glycinergic presynaptic nerve terminals occur during postnatal development. 2. ATP facilitated glycinergic mIPSC frequency in a concentration-dependent manner through all developmental stages tested, whereas alphabeta-methylene-ATP (alphabeta-me-ATP) was only effective at later developmental stages. 3. alphabeta-me-ATP-elicited mIPSC frequency facilitation was completely occluded in the Ca2+-free external solution, but it was not affected by adding 10(-4) M Cd2+. 4. alphabeta-me-ATP still facilitated mIPSC frequency even in the presence of 10(-6) M thapsigargin, a Ca2+ pump blocker. 5. In later developmental stages, ATP-elicited presynaptic or postsynaptic responses were reversibly blocked by 10(-5) M pyridoxal-5-phosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulfonic acid (PPADS), but only partially blocked by 10(-7) M 2',3'-O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-ATP (TNP-ATP). However, alphabeta-me-ATP-elicited presynaptic or postsynaptic responses were completely and reversibly blocked by either 10(-5) M PPADS or 10(-7) M TNP-ATP. 6. alphabeta-me-ATP significantly reduced the evoked glycinergic IPSC amplitude in postnatal 28-30 day neurones, whereas it had no effect in 10-12 day neurones. 7. It was concluded that alphabeta-me-ATP-sensitive P2X receptors were functionally expressed on the glycinergic presynaptic nerve terminals projecting to SG neurones in later developmental stages. Such developmental changes of presynaptic P2X receptor subtypes might contribute to synaptic plasticity such as the regulation of neuronal excitability and the fine controlling of the pain signal in spinal dorsal horn neurones.
Figures








Similar articles
-
ATP facilitates spontaneous glycinergic IPSC frequency at dissociated rat dorsal horn interneuron synapses.J Physiol. 2000 Apr 15;524 Pt 2(Pt 2):471-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00471.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10766927 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic and vanilloid receptor activation releases glutamate from separate cranial afferent terminals in nucleus tractus solitarius.J Neurosci. 2004 May 19;24(20):4709-17. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0753-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15152030 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiation of inhibitory glycinergic neurotransmission by Zn2+: a synergistic interplay between presynaptic P2X2 and postsynaptic glycine receptors.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Sep;16(6):1025-36. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02170.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12383231
-
P2-purinoceptors on postganglionic sympathetic neurones.J Auton Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;16(6):413-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1996.tb00065.x. J Auton Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 9131428 Review.
-
Neuronal P2 receptors of the central nervous system.Curr Top Med Chem. 2004;4(8):831-8. doi: 10.2174/1568026043451032. Curr Top Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15078214 Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleotide signaling in nervous system development.Pflugers Arch. 2006 Aug;452(5):573-88. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0067-4. Epub 2006 Apr 25. Pflugers Arch. 2006. PMID: 16639549 Review.
-
Cell Type-Specific Expression of Purinergic P2X Receptors in the Hypothalamus.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 22;26(11):5007. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115007. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct excitation of deep dorsal horn neurones in the rat spinal cord by the activation of postsynaptic P2X receptors.J Physiol. 2006 Jun 15;573(Pt 3):753-63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.108613. Epub 2006 Apr 13. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16613873 Free PMC article.
-
Fast synaptic inhibition in spinal sensory processing and pain control.Physiol Rev. 2012 Jan;92(1):193-235. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00043.2010. Physiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22298656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Effects of Alpha 1-Adrenoceptor Antagonists on the Postsynaptic Sensitivity: Using Slice Patch-Clamp Technique for Inhibitory Postsynaptic Current in Substantia Gelatinosa Neurons From Lumbosacral Spinal Cord in Rats.Int Neurourol J. 2020 Jun;24(2):127-134. doi: 10.5213/inj.1938248.124. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Int Neurourol J. 2020. PMID: 32615674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaike N, Harata N. Nystatin perforated patch recording and its application to analysis of intracellular mechanism. Japanese Journal of Physiology. 1994;44:433–473. - PubMed
-
- Bo X, Burnstock G. Distribution of [3H]α,β-methylene ATP binding sites in rat brain and spinal cord. NeuroReport. 1994;5:1601–1604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

