UP element-dependent transcription at the Escherichia coli rrnB P1 promoter: positional requirements and role of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit linker
- PMID: 11600705
- PMCID: PMC60210
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.20.4166
UP element-dependent transcription at the Escherichia coli rrnB P1 promoter: positional requirements and role of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit linker
Abstract
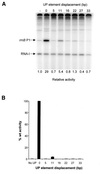
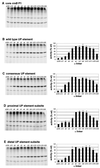
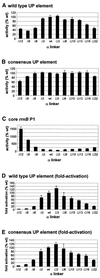
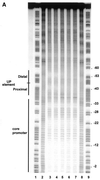
The UP element stimulates transcription from the rrnB P1 promoter through a direct interaction with the C-terminal domain of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit (alphaCTD). We investigated the effect on transcription from rrnB P1 of varying both the location of the UP element and the length of the alpha subunit interdomain linker, separately and in combination. Displacement of the UP element by a single turn of the DNA helix resulted in a large decrease in transcription from rrnB P1, while displacement by half a turn or two turns totally abolished UP element-dependent transcription. Deletions of six or more amino acids from within the alpha subunit linker resulted in a decrease in UP element-dependent stimulation, which correlated with decreased binding of alphaCTD to the UP element. Increasing the alpha linker length was less deleterious to RNA polymerase function at rrnB P1 but did not compensate for the decrease in activation that resulted from displacing the UP element. Our results suggest that the location of the UP element at rrnB P1 is crucial to its function and that the natural length of the alpha subunit linker is optimal for utilisation of the UP element at this promoter.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang G., Campbell,E.A., Minakhin,L., Richter,C., Severinov,K. and Darst,S.A. (1999) Crystal structure of Thermus aquaticus core RNA polymerase at 3.3 Å resolution. Cell, 98, 811–824. - PubMed
-
- Ebright R.H. (2000) RNA polymerase: structural similarities between bacterial RNA polymerase and eucaryotic RNA polymerase II. J. Mol. Biol., 304, 687–698. - PubMed
-
- Darst S.A., Roberts,J.W., Malhotra,A., Mark,M., Severinov,K. and Severinova,E. (1997) Pribnow box recognition and melting by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. In Eckstein,F. and Lilley,D.M.J. (eds), Nucleic Acids and Molecular Biology, Vol. 11. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 27–40.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

