Proton exchange and local stability in a DNA triple helix containing a G.TA triad
- PMID: 11600712
- PMCID: PMC60212
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.20.4231
Proton exchange and local stability in a DNA triple helix containing a G.TA triad
Abstract
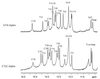
Recognition of a thymine-adenine base pair in DNA by triplex-forming oligonucleotides can be achieved by a guanine through the formation of a G.TA triad within the parallel triple helix motif. In the present work, we provide the first characterization of the stability of individual base pairs and base triads in a DNA triple helix containing a G.TA triad. The DNA investigated is the intramolecular triple helix formed by the 32mer d(AGATAGAACCCCTTCTATCTTATATCTGTCTT). The exchange rates of imino protons in this triple helix have been measured by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using magnetization transfer from water and real-time exchange. The exchange rates are compared with those in a homologous DNA triple helix in which the G.TA triad is replaced by a canonical C(+).GC triad. The results indicate that, in the G.TA triad, the stability of the Watson-Crick TA base pair is comparable with that of AT base pairs in canonical T.AT triads. However, the presence of the G.TA triad destabilizes neighboring triads by 0.6-1.8 kcal/mol at 1 degrees C. These effects extend to triads that are two positions removed from the site of the G.TA triad. Therefore, the lower stability of DNA triple helices containing G.TA triads originates, in large part, from the energetic effects of the G.TA triad upon the stability of canonical triads located in its vicinity.
Figures
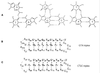


Similar articles
-
Site-resolved energetics in DNA triple helices containing G*TA and T*CG triads.Biochemistry. 2002 Apr 2;41(13):4407-14. doi: 10.1021/bi011832s. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 11914088
-
Proton exchange and base pair opening in a DNA triple helix.Biochemistry. 2001 Sep 18;40(37):11065-72. doi: 10.1021/bi010890a. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11551203
-
NMR structural studies of intramolecular (Y+)n.(R+)n(Y-)nDNA triplexes in solution: imino and amino proton and nitrogen markers of G.TA base triple formation.Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 17;30(37):9022-30. doi: 10.1021/bi00101a016. Biochemistry. 1991. PMID: 1654085
-
Kinetics for exchange of imino protons in the d(C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G) double helix and in two similar helices that contain a G . T base pair, d(C-G-T-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G), and an extra adenine, d(C-G-C-A-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G).Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6567-74. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a038. Biochemistry. 1982. PMID: 6295469
-
Time delay during the proton tunneling in the base pairs of the DNA double helix.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2021 Dec;167:96-103. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34118266 Review.
Cited by
-
The Development of Non-natural Type Nucleoside to Stabilize Triplex DNA Formation against CG and TA Inversion Site.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(19):2663-2686. doi: 10.2174/0929867330666230512114130. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37183460 Review.
-
Dynamics Studies of DNA with Non-canonical Structure Using NMR Spectroscopy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 11;21(8):2673. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082673. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32290457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic modulation of endogenous gene function by agents with designed DNA-sequence specificities.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Nov 1;31(21):6064-78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg815. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 14576293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-resolved stabilization of a DNA triple helix by magnesium ions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Feb 9;32(3):878-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh228. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 14769945 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of 5-N-carboxamide modifications on the thermodynamic stability of oligonucleotides.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 30;43(19):9107-22. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv981. Epub 2015 Oct 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26438535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soyfer V.N. and Potaman,V.N. (1995) Triple-Helical Nucleic Acids. Springer, New York, NY.
-
- Cooney M., Czernuszewicz,G., Postel,E.H., Flint,S.J. and Hogan,M.E. (1988) Site-specific oligonucleotide binding represses transcription of the human c-myc gene in vitro. Science, 241, 456–459. - PubMed
-
- Vasquez K.M. and Wilson,J.H. (1998) Triplex-directed modification of genes and gene activities. Trends Biochem. Sci., 23, 4–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

