Structural features underlying selective inhibition of protein kinase CK2 by ATP site-directed tetrabromo-2-benzotriazole
- PMID: 11604527
- PMCID: PMC2374052
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.19601
Structural features underlying selective inhibition of protein kinase CK2 by ATP site-directed tetrabromo-2-benzotriazole
Abstract
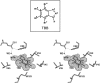
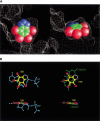
Two novel crystal structures of Zea mays protein kinase CK2alpha catalytic subunit, one in complex with the specific inhibitor 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole (TBB) and another in the apo-form, were solved at 2.2 A resolution. These structures were compared with those of the enzyme in presence of ATP and GTP (the natural cosubstrates) and the inhibitor emodin. Interaction of TBB with the active site of CK2alpha is mainly due to van der Waals contacts, with the ligand fitting almost perfectly the cavity. One nitrogen of the five-membered ring interacts with two charged residues, Glu 81 and Lys 68, in the depth of the cavity, through two water molecules. These are buried in the active site and are also generally found in the structures of CK2alpha enzyme analyzed so far, with the exception of the complex with emodin. In the N-terminal lobe, the position of helix alphaC is particularly well preserved in all the structures examined; the Gly-rich loop is displaced from the intermediate position it has in the apo-form and in the presence of the natural cosubstrates (ATP/GTP) to either an upper (with TBB) or a lower position (with emodin). The selectivity of TBB for CK2 appears to be mainly dictated by the reduced size of the active site which in most other protein kinases is too large for making stable interactions with this inhibitor.
Figures

References
-
- Allende, J.E. and Allende, C.C. 1995. Protein kinase CK2: An enzyme with multiple substrates and a puzzling regulation. FASEB J. 9 313–323. - PubMed
-
- Battistutta, R., Sarno, S., De Moliner, E., Papinutto, E., Zanotti, G., and Pinna, L.A. 2000. The replacement of ATP by the competitive inhibitor emodin induces conformational modifications in the catalytic site of protein kinase CK2. J. Biol. Chem. 27529618–29622. - PubMed
-
- Brunger, A.T., Adams, P.D., Clore, G.M., DeLano, W.L., Gros, P., Grosse Kunstleve, R.W., Jiang, J.S., Kuszewski, J., Nilges, M., Pannu, N.S., Read, R.J., Rice, L.M., Simonson, T., and Warren, G.L. 1998. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54 905–921. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, P. 1999. The development and therapeutic potential of protein kinase inhibitors. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 3 459–465. - PubMed
-
- De Azevedo, W.F., Leclerc, S., Meijer, L., Havlicek, L., Strnad, M., and Kim, S.H. 1997. Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by purine analogues: Crystal structure of human cdk2 complexed with roscovitine. Eur. J. Biochem. 243 518–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

