Effects of dantrolene and its derivatives on Ca(2+) release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of mouse skeletal muscle fibres
- PMID: 11606312
- PMCID: PMC1573001
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704307
Effects of dantrolene and its derivatives on Ca(2+) release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of mouse skeletal muscle fibres
Abstract
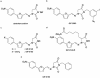
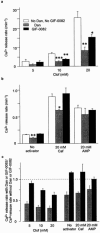
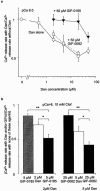
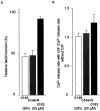
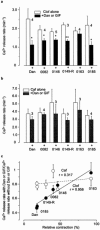
1. We analysed the effect of dantrolene (Dan) and five newly synthesized derivatives (GIFs) on Ca(2+) release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) of mouse skeletal muscle. 2. In intact muscles, GIF-0185 reduced the size of twitch contraction induced by electrical stimulation to the same extent as Dan. GIF-0082, an azido-functionalized Dan derivative, also inhibited twitch contraction, although the extent of inhibition was less than that of Dan and of GIF-0185. 3. In skinned fibres, Dan inhibited Ca(2+)-induced Ca(2+) release (CICR) under Mg(2+)-free conditions at room temperature. In contrast, GIF-0082 and GIF-0185 showed no inhibitory effect on CICR under the same conditions. 4. Dan-induced inhibition of CICR was not affected by the presence of GIF-0082, whereas it was diminished in the presence of GIF-0185. 5. GIF-0082 and GIF-0185 significantly inhibited clofibric acid (Clof)-induced Ca(2+) release, as did Dan. 6. Several Dan derivatives other than GIF-0082 and GIF-0185 showed an inhibitory effect on twitch tension but not on the CICR mechanism. All of these derivatives inhibited Clof-induced Ca(2+) release. 7. The magnitudes of inhibition of Clof-induced Ca(2+) release by all Dan derivatives were well correlated with those of twitch inhibition. This supports the notion that the mode of Clof-induced opening of the RyR-Ca(2+) release channel may be similar to that of physiological Ca(2+) release (PCR). 8. These results indicate that the difference in opening modes of the RyR-Ca(2+) release channel is recognized by certain Dan derivatives.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Properties of Ca(2+) release induced by clofibric acid from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of mouse skeletal muscle fibres.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Oct;134(4):719-28. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704306. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11606311 Free PMC article.
-
Dantrolene analogues revisited: general synthesis and specific functions capable of discriminating two kinds of Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum of mouse skeletal muscle.Bioorg Med Chem. 2003 Mar 6;11(5):663-73. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(02)00600-4. Bioorg Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12537995
-
[(125)I]-N-[(3-azido-5-iodo)benzyl]dantrolene and [(125)I]-N-[[3-iodo-5-(3-trifluoromethyl-3H-diazirin-3-yl)]benzyl]dantrolene: photoaffinity probes specific for the physiological Ca(2+) release from sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2002 Nov 18;12(22):3263-5. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(02)00701-1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2002. PMID: 12392728
-
Mechanisms of the UTP-induced tension in mammalian skeletal muscles.Acta Physiol Pharmacol Ther Latinoam. 1999;49(4):224-32. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Ther Latinoam. 1999. PMID: 10797865 Review.
-
Calcium-induced calcium release in skeletal muscle.Physiol Rev. 2009 Oct;89(4):1153-76. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00040.2008. Physiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19789379 Review.
Cited by
-
Properties of Ca(2+) release induced by clofibric acid from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of mouse skeletal muscle fibres.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Oct;134(4):719-28. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704306. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11606311 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role of neuroendocrine-specific protein-like 1 in membrane translocation of GLUT4.Diabetes. 2009 Dec;58(12):2802-12. doi: 10.2337/db09-0756. Epub 2009 Aug 31. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19720795 Free PMC article.
-
Osmosensation in TRPV2 dominant negative expressing skeletal muscle fibres.J Physiol. 2015 Sep 1;593(17):3849-63. doi: 10.1113/JP270522. Epub 2015 Aug 10. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26108786 Free PMC article.
-
Ryanodine receptor RyR1-mediated elevation of Ca2+ concentration is required for the late stage of myogenic differentiation and fusion.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022 Feb 11;13(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s40104-021-00668-x. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35144690 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical, morphological and genetic characterization of Brody disease: an international study of 40 patients.Brain. 2020 Feb 1;143(2):452-466. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz410. Brain. 2020. PMID: 32040565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BARRACLOUGH P., BROCKWELL M., CALDWELI A.G., DEMAINE D.A., HARRIS C.J., KING W.R., STEPNEY R.J., WHARTON C.J., WHITTLE B.J.R. Synthesis and inhibitory activity on platelet aggregation of 13′-aza and other ω-chain modified BW245C analogs. Arch. Pharmacol. 1994;327:307–317. - PubMed
-
- BERS D.M., PEREZ-REYES E. Ca channels in cardiac myocytes: structure and function in Ca influx and intracellular Ca release. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999;42:339–360. - PubMed
-
- DENAT F., GASPARD-ILOUGHMANE H., DUBAC J. An easy one-pot synthesis of group 14 C-metallated 2 (or 3)-furan- and thiophenecarbaldehydes. Synthesis. 1992;1992:954–956.
-
- ELLIS K.O., BRYANT S.H. Excitation-contraction uncoupling in skeletal muscle by dantrolene sodium. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1972;274:107–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

