The effects of heparin on the adhesion of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells to human stimulated umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMID: 11606323
- PMCID: PMC1573012
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704321
The effects of heparin on the adhesion of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells to human stimulated umbilical vein endothelial cells
Abstract
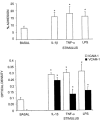
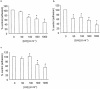
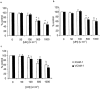
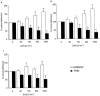
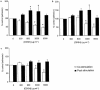
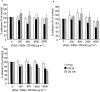
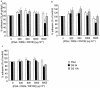
1. The effects of unfractionated heparin (UH) and a selectively O-desulphated derivative of heparin (ODSH), lacking anticoagulant activity, on the adhesion of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (HPBMNC) to human stimulated umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), were investigated. 2. For comparison, the effects of poly-L-glutamic acid (PGA), a large polyanionic molecule without sulphate groups and two different molecular weight sulphated dextrans (DS 5 k and DS 10 k) were studied. 3. UH (50 - 1000 u ml(-1)) significantly (P<0.05) inhibited the adhesion of HPBMNC to HUVECs, stimulated with IL-1beta (100 u ml(-1)), TNF-alpha (1000 u ml(-1)) or LPS (100 microg ml(-1)), when the drugs were added together with stimuli to HUVECs and coincubated for 6 h. Such effects on adhesion occurred with limited influence on expression of relevant endothelial adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1). 4. UH (100 - 1000 u ml(-1)), when added to prestimulated HUVECs, significantly (P<0.05) increased adhesion of mononuclear cells to endothelium at the higher concentrations tested, without any effect on adhesion molecule expression. In contrast, the opposite effect was observed when human polymorphonuclear leucocyte adhesion was examined, under the same experimental conditions, suggesting that the observed potentiation of HPBMNC adhesion is cell specific. 5. The effects of UH on HPBMNC adhesion were shared by the non-anticoagulant ODSH (600 - 6000 microg ml(-1)) but not by sulphated dextrans or PGA (300 - 6000 microg ml(-1)). 6. Heparin affects the adhesion of HPBMNC to stimulated endothelium, in both an inhibitory and potentiating manner, effects which are unrelated to its anticoagulant activity and not solely dependent on molecular charge characteristics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of heparin and related molecules upon the adhesion of human polymorphonuclear leucocytes to vascular endothelium in vitro.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Feb;129(3):533-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703099. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10711352 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine could augment adhesion molecule expression in human endothelial cells through macrophages secreting TNF-alpha, IL-1beta.Int Immunopharmacol. 2004 Dec 15;4(13):1675-86. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2004.07.028. Int Immunopharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15454119
-
Protocatechuic aldehyde suppresses TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Apr 18;513(1-2):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.01.059. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15878704
-
Inhibitory effects of bucillamine on the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2004 Jan;4(1):119-26. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2003.11.002. Int Immunopharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14975366
-
Hesperidin, hesperidin methyl chalone and phellopterin from Poncirus trifoliata (Rutaceae) differentially regulate the expression of adhesion molecules in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2008 May;8(5):670-8. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2008.01.011. Epub 2008 Feb 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18387509
Cited by
-
Heparanase: A Novel Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Atherosclerosis.Cells. 2022 Oct 12;11(20):3198. doi: 10.3390/cells11203198. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heparin and related drugs: beyond anticoagulant activity.ISRN Pharmacol. 2013 Jul 30;2013:910743. doi: 10.1155/2013/910743. eCollection 2013. ISRN Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23984092 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte Heparanase: A Double-Edged Sword in Tumor Progression.Front Oncol. 2019 Apr 29;9:331. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00331. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31110966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Size-fractionated heparins have differential effects on human neutrophil function in vitro.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;151(6):837-43. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707298. Epub 2007 May 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17533420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AHMED T., CAMPO C., ABRAHAM M.K., MOLINAR I.J.F., ABRAHAM W.M., ASHKIN D., SYRISTE T., ANDERSSON L.O., SVAHN C.M. Inhibition of antigen-induced acute bronchoconstriction, airway hyperresponsiveness, and mast cell degranulation by a nonanticoagulant heparin: comparison with a low molecular weight heparin. Am. J. Respir. Cri. Care. Med. 1997;155:1848–1855. - PubMed
-
- AHMED T., UNGO J., ZHOU M., CAMPO C. Inhibition of allergic late airways responses by inhaled heparin-derived oligosaccharides. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000;88:1721–1729. - PubMed
-
- BAR-NER M., ELDOR A., WASSERMAN L., MATZNER Y., COHEN I.R., FUKS Z., VLODAVSKY I. Inhibition of heparanase-mediated degradation of extracellular matrix heparan sulfate by non-anticoagulant heparin. Blood. 1987;70:551–557. - PubMed
-
- BAZZONI G., NUÑEZ A.B., MASCELLANI G., BIANCHINI P., DEJANA E., DEL MASCHIO A. Effect of heparin, dermatan sulfate, and related oligo-derivatives on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte functions. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1992;121:268–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

