Sodium channel mRNAs at the neuromuscular junction: distinct patterns of accumulation and effects of muscle activity
- PMID: 11606634
- PMCID: PMC6762790
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-21-08456.2001
Sodium channel mRNAs at the neuromuscular junction: distinct patterns of accumulation and effects of muscle activity
Abstract
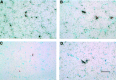
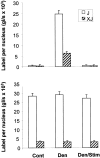
Voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs) are highly concentrated at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) in mammalian skeletal muscle. Here we test the hypothesis that local upregulation of mRNA contributes to this accumulation. We designed radiolabeled antisense RNA probes, specific for the "adult" Na(V)1.4 and "fetal" Na(V)1.5 isoforms of VGSC in mammalian skeletal muscle, and used them in in situ hybridization studies of rat soleus muscles. Na(V)1.4 mRNA is present throughout normal adult muscles but is highly concentrated at the NMJ, in which the amount per myonucleus is more than eightfold greater than away from the NMJ. Na(V)1.5 mRNA is undetectable in innervated muscles but is dramatically upregulated by denervation. In muscles denervated for 1 week, both Na(V)1.4 and Na(V)1.5 mRNAs are present throughout the muscle, and both are concentrated at the NMJ. No Na(V)1.5 mRNA was detectable in denervated muscles stimulated electrically for 1 week in vivo. Neither denervation nor stimulation had any significant effect on the level or distribution of Na(V)1.4 mRNA. We conclude that factors, probably derived from the nerve, lead to the increased concentration of VGSC mRNAs at the NMJ. In addition, the expression of Na(V)1.5 mRNA is downregulated by muscle activity, both at the NMJ and away from it.
Figures



References
-
- Bowen DC, Park SJ, Bodine S, Stark JL, Valenzuela DM, Stitt TN, Yancopoulos GD, Lindsay RM, Glass DJ, DiStefano PS. Localization and regulation of Musk at the neuromuscular junction. Dev Biol. 1998;199:309–319. - PubMed
-
- Buonanno A, Fields RD. Gene regulation by patterned electrical activity during neural and skeletal muscle development. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1999;9:110–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
