Epithelial antimicrobial peptides in host defense against infection
- PMID: 11667978
- PMCID: PMC59560
- DOI: 10.1186/rr25
Epithelial antimicrobial peptides in host defense against infection
Abstract
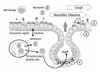
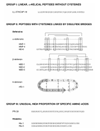
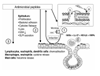
One component of host defense at mucosal surfaces seems to be epithelium-derived antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrobial peptides are classified on the basis of their structure and amino acid motifs. Peptides of the defensin, cathelicidin, and histatin classes are found in humans. In the airways, alpha-defensins and the cathelicidin LL-37/hCAP-18 originate from neutrophils. beta-Defensins and LL-37/hCAP-18 are produced by the respiratory epithelium and the alveolar macrophage and secreted into the airway surface fluid. Beside their direct antimicrobial function, antimicrobial peptides have multiple roles as mediators of inflammation with effects on epithelial and inflammatory cells, influencing such diverse processes as proliferation, immune induction, wound healing, cytokine release, chemotaxis, protease-antiprotease balance, and redox homeostasis. Further, antimicrobial peptides qualify as prototypes of innovative drugs that might be used as antibiotics, anti-lipopolysaccharide drugs, or modifiers of inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Fearon D, Locksley R. The instructive role of innate immunity in the aquired immune response. Science. 1996;272:50–54. - PubMed
-
- Wilmott R, Fiedler M, Stark J. Host defense mechanisms. . In Disorders of the Respiratory Tract in Children Edited by Chernick V, Boat TF Philadelphia: Saunders; 1998. pp. 238–264.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

