Genomewide multipoint linkage analysis of seven extended Palauan pedigrees with schizophrenia, by a Markov-chain Monte Carlo method
- PMID: 11668428
- PMCID: PMC1235540
- DOI: 10.1086/324590
Genomewide multipoint linkage analysis of seven extended Palauan pedigrees with schizophrenia, by a Markov-chain Monte Carlo method
Abstract
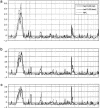
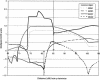
Palauans are an isolated population in Micronesia with lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia (SCZD) of 2%, compared to the world rate of approximately 1%. The possible enrichment for SCZD genes, in conjunction with the potential for reduced etiological heterogeneity and the opportunity to ascertain statistically powerful extended pedigrees, makes Palauans a population of choice for the mapping of SCZD genes. We have used a Markov-chain Monte Carlo method to perform a genomewide multipoint analysis in seven extended pedigrees from Palau. Robust multipoint parametric and nonparametric linkage (NPL) analyses were performed under three nested diagnostic classifications-core, spectrum, and broad. We observed four regions of interest across the genome. Two of these regions-on chromosomes 2p13-14 (for which, under core diagnostic classification, NPL=6.5 and parametric LOD=4.8) and 13q12-22 (for which, under broad diagnostic classification, parametric LOD=3.6, and, under spectrum diagnostic classification, parametric LOD=3.5)-had evidence for linkage with genomewide significance, after correction for multiple testing; with the current pedigree resource and genotyping, these regions are estimated to be 4.3 cM and 19.75 cM in size, respectively. A third region, with intermediate evidence for linkage, was identified on chromosome 5q22-qter (for which, under broad diagnostic classification, parametric LOD=2.5). The fourth region of interest had only borderline suggestive evidence for linkage (on 3q24-28; for this region, under broad diagnostic classification, parametric LOD=2.0). All regions exhibited evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Our findings provide significant evidence for susceptibility loci on chromosomes 2p13-14 and 13q12-22 and support both a model of genetic heterogeneity and the utility of a broader set of diagnostic classifications in the population from Palau.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/
-
- Cooperative Human Linkage Center, The, http://lpg.nci.nih.gov/CHLC/
-
- Genome Database, The, http://gdbwww.gdb.org/ (for information on genetic mapping)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for SCZD [MIM 181500])
References
-
- Abkevich V, Camp NJ, Gutin A, Farnham JM, Cannon-Albright L, Thomas A. A robust multipoint linkage statistic (TLOD) for mapping complex trait loci. Genet Epidemiol (in press) - PubMed
-
- Baron M, Gruen R, Asnis L, Kane J (1982) Schizoaffective illness, schizophrenia and affective disorders: morbidity risk and genetic transmission. Acta Psychiatr Scand 65:253–262 - PubMed
-
- Bennett PJ, Hoff M, Rosenthal J, Zhao M, Coon H, Myles-Worsley M, Byerley W (2000) Mutation screening of a neutral amino acid transporter, ASCT1, and its potential role in schizophrenia. Psychiatr Genet 10:79–82 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

