Use of abciximab for mediation of thromboembolic complications of endovascular therapy
- PMID: 11673176
- PMCID: PMC7974456
Use of abciximab for mediation of thromboembolic complications of endovascular therapy
Abstract
We describe four cases in which abciximab was used as a thrombolytic rescue agent in the setting of thrombotic events complicating interventional neuroradiologic procedures. After IV administration of abciximab, the thrombus resolved within 30 min in three cases, whereas no thrombolysis occurred in the fourth case despite the addition of intraarterial tissue plasminogen activator. Further evaluation of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa inhibitors in patients with cerebral thromboembolic events is necessary to prove clinical efficacy.
Figures
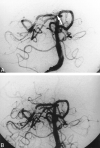
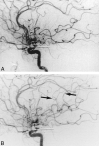


References
-
- Lempert TE, Malek AM, Halbach VV, Phatouros CC, Dowd CF, Higashida RT. Rescue treatment of acute parent vessel thrombosis with glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor during GDC coil embolization. Stroke 1999;30:693-695 - PubMed
-
- Samuels OB, Mohomed Y, Miller D, et al. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty plus abciximab for vertebrobasilar stenosis. Presented at: American Society of Interventional and Therapeutic Neuroradiology meeting; January 1999
-
- The Abciximab in Ischemic Stroke Investigators. Abciximab in acute ischemic stroke: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation study. Stroke 2000;31:601-609 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
