Identification and characterization of the three chitin-binding domains within the multidomain chitinase Chi92 from Aeromonas hydrophila JP101
- PMID: 11679332
- PMCID: PMC93277
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.11.5100-5106.2001
Identification and characterization of the three chitin-binding domains within the multidomain chitinase Chi92 from Aeromonas hydrophila JP101
Abstract
The gene (chi92) encoding the extracellular chitinase of Aeromonas hydrophila JP101 has been cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The mature form of Chi92 is an 842-amino-acid (89.830-kDa) modular enzyme comprised of a family 18 catalytic domain, an unknown-function region (the A region), and three chitin-binding domains (ChBDs; Chi92-N, ChBD(CI), and ChBD(CII)). The C-terminally repeated ChBDs, ChBD(CI) and ChBD(CII), were grouped into family V of cellulose-binding domains on the basis of sequence homology. Chitin binding and enzyme activity studies with C-terminally truncated Chi92 derivatives lacking ChBDs demonstrated that the ChBDs are responsible for its adhesion to unprocessed and colloidal chitins. Further adsorption experiments with glutathione S-transferase (GST) fusion proteins (GST-CI and GST-CICII) demonstrated that a single ChBD (ChBD(CI)) could promote efficient chitin and cellulose binding. In contrast to the two C-terminal ChBDs, the Chi92-N domain is similar to ChiN of Serratia marcescens ChiA, which has been proposed to participate in chitin binding. A truncated derivative of Chi92 that contained only a catalytic domain and Chi92-N still exhibited insoluble-chitin-binding and hydrolytic activities. Thus, it appears that Chi92 contains Chi92-N as the third ChBD in addition to two ChBDs (ChBD(CI) and ChBD(CII)).
Figures


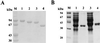
Similar articles
-
Biochemical characterization and site-directed mutational analysis of the double chitin-binding domain from chitinase 92 of Aeromonas hydrophila JP101.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004 Mar 12;232(1):61-6. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(04)00014-X. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15019735
-
Family 19 chitinase from Aeromonas sp. No.10S-24: role of chitin-binding domain in the enzymatic activity.J Biochem. 2005 Feb;137(2):235-42. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvi022. J Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15749838
-
The C-terminal module of Chi1 from Aeromonas caviae CB101 has a function in substrate binding and hydrolysis.Proteins. 2003 Dec 1;53(4):908-16. doi: 10.1002/prot.10501. Proteins. 2003. PMID: 14635132
-
Cell surface display of Chi92 on Escherichia coli using ice nucleation protein for improved catalytic and antifungal activity.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006 Mar;256(1):119-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00115.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16487328
-
Chitin and chitinase: Role in pathogenicity, allergenicity and health.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Apr;97:331-338. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.042. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 28093332 Review.
Cited by
-
Chitinases of Bacillus thuringiensis: Phylogeny, Modular Structure, and Applied Potentials.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 14;10:3032. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03032. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31993038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cloning and expression analysis of the chitinase gene Ifu-chit2 from Isaria fumosorosea.Genet Mol Biol. 2015 Jul-Sep;38(3):381-9. doi: 10.1590/S1415-475738320150003. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Genet Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26500443 Free PMC article.
-
SGBP-B-like bimodular cellulose-binding protein CHU_1279 is essential for cellulose utilization by Cytophaga hutchinsonii.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Apr 23;91(4):e0247124. doi: 10.1128/aem.02471-24. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40130838 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning and purification of an endochitinase from Serratia marcescens (Nima).Mol Biotechnol. 2005 Oct;31(2):103-11. doi: 10.1385/MB:31:2:103. Mol Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 16170210
-
Putative exposed aromatic and hydroxyl residues on the surface of the N-terminal domains of Chi1 from Aeromonas caviae CB101 are essential for chitin binding and hydrolysis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Nov;71(11):7559-61. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.11.7559-7561.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16269803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beggs J D. Transformation of yeast by a replicating hybrid plasmid. Nature. 1978;275:104–109. - PubMed
-
- Blaak H, Schrempf H. Binding and Substrate specificities of a Streptomyces olivaceoviridis chitinase in comparison with its proteolytically processed form. Eur J Biochem. 1995;229:132–139. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Brun E, Moriaud F, Gans P, Blackledge M J, Barras F, Marion D. Solution structure of the cellulose-binding domain of the endoglucanase Z secreted by Erwinia chrysanthemi. Biochemistry. 1997;36:16074–16086. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

