An altered Pseudomonas diversity is recovered from soil by using nutrient-poor Pseudomonas-selective soil extract media
- PMID: 11679350
- PMCID: PMC93295
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.11.5233-5239.2001
An altered Pseudomonas diversity is recovered from soil by using nutrient-poor Pseudomonas-selective soil extract media
Abstract
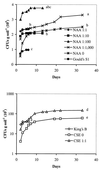
We designed five Pseudomonas-selective soil extract NAA media containing the selective properties of trimethoprim and sodium lauroyl sarcosine and 0 to 100% of the amount of Casamino Acids used in the classical Pseudomonas-selective Gould's S1 medium. All of the isolates were confirmed to be Pseudomonas by a Pseudomonas-specific OprF antibody and a Pseudomonas-specific PCR targeting 16S ribosomal DNA. The Pseudomonas isolates were characterized by classical physiological tests, repetitive extragenic palindromic-PCR, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and carbon source utilization patterns. Several of these analyses showed that the amount of Casamino Acids significantly influenced the diversity of the recovered Pseudomonas isolates. Furthermore, the data suggested that specific Pseudomonas subpopulations were represented on the nutrient-poor media. The NAA 1:100 medium, containing ca. 15 mg of organic carbon per liter, consistently gave significantly higher Pseudomonas CFU counts than Gould's S1 when tested on four Danish soils. NAA 1:100 may, therefore, be a better medium than Gould's S1 for enumeration and isolation of Pseudomonas from the low-nutrient soil environment.
Figures

References
-
- Andersen S M, Johnsen K, Sørensen J, Nielsen P, Jacobsen C S. Pseudomonas frederiksbergensis sp. nov., isolated from soil at a coal gasification site. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000;50:1957–1964. - PubMed
-
- Andersen S M, Jørgensen C, Jacobsen C S. Development and utilisation of a medium to isolate phenanthrene-degrading Pseudomonas spp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001;55:112–116. - PubMed
-
- Buck J D. Effects of medium composition on the recovery of bacteria from sea water. J Exp Marine Biol Ecol. 1974;15:25–34.
-
- de Bruijn F J. Use of repetitive (repetitive extragenic palindromic and enterobacterial repetitive intergeneric consensus) sequences and the polymerase chain reaction to fingerprint the genomes of Rhizobium meliloti isolates and other soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992;58:2180–2187. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

