Differential and age-dependent expression of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel isoforms 1-4 suggests evolving roles in the developing rat hippocampus
- PMID: 11682156
- PMCID: PMC3084019
- DOI: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00314-1
Differential and age-dependent expression of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel isoforms 1-4 suggests evolving roles in the developing rat hippocampus
Abstract
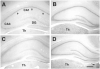
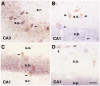
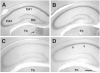
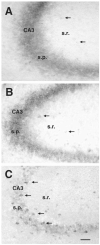
Hyperpolarization-activated cation currents (I(h)) are found in several brain regions including thalamus and hippocampus. Important functions of these currents in promoting synchronized network activity and in determining neuronal membrane properties have been progressively recognized, but the molecular underpinnings of these currents are only emerging. I(h) currents are generated by hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels (HCNs). These channel proteins are encoded by at least four HCN genes, that govern the kinetic and functional properties of the resulting channels. Because of the potential impact of I(h)-mediated coordinated neuronal activity on the maturation of the functional hippocampal network, this study focused on determining the expression of the four members of the HCN gene family throughout postnatal hippocampal development at both the regional and single cell level.The results of these experiments demonstrated that HCNs 1, 2 and 4 are differentially expressed in interneuronal and principal cell populations of the rat hippocampal formation. Expression profiles of each HCN isoform evolve during postnatal development, and patterns observed during early postnatal ages differ significantly from those in mature hippocampus. The onset of HCN expression in interneurons of the hippocampus proper precedes that in the dentate gyrus, suggesting that HCN-mediated pacing activity may be generated in hippocampal interneurons prior to those in the hilus. Taken together, these findings indicate an age-dependent spatiotemporal evolution of specific HCN expression in distinct hippocampal cell populations, and suggest that these channels serve differing and evolving functions in the maturation of coordinated hippocampal activity.
Figures

References
-
- Bayer SA. Development of the hippocampal region in the rat. I. Neurogenesis examined with [3H]thymidine autoradiography. J. Comp. Neurol. 1980;195:51–86. - PubMed
-
- Bender R, Hoffmann MC, Frotscher M, Nitsch C. Species-specific expression of parvalbumin in the entorhinal cortex of the Mongolian gerbil: dependence on local activity but not extrinsic afferents. Neuroscience. 2000;99:423–431. - PubMed
-
- Blasco-Ibanez JM, Freund TF. Synaptic input of horizontal interneurons in stratum oriens of the hippocampal CA1 subfield: structural basis of feed-back activation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1995;7:2170–2180. - PubMed
-
- Clapham DE. Not so funny anymore: pacing channels are cloned. Neuron. 1998;21:5–7. - PubMed

