Protein kinase C involvement in aloe-emodin- and emodin-induced apoptosis in lung carcinoma cell
- PMID: 11682458
- PMCID: PMC1573035
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704342
Protein kinase C involvement in aloe-emodin- and emodin-induced apoptosis in lung carcinoma cell
Abstract
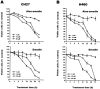
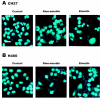
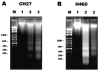
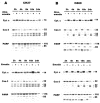
1. This study demonstrated aloe-emodin- and emodin-induced apoptosis in lung carcinoma cell lines CH27 (human lung squamous carcinoma cell) and H460 (human lung non-small cell carcinoma cell). Aloe-emodin- and emodin-induced apoptosis was characterized by nuclear morphological changes and DNA fragmentation. 2. During apoptosis, an increase in cytochrome c of cytosolic fraction and activation of caspase-3, identified by the cleavage of its proform, were observed. 3. To elucidate whether the expression of protein kinase C (PKC) isozymes are involved in aloe-emodin- and emodin-induced apoptosis, this study examined the changes of PKC isozymes by Western blotting techniques during aloe-emodin- and emodin-induced apoptosis. 4. The expression of PKC isozymes involved in aloe-emodin- and emodin-induced apoptosis of CH27 and H460 cells. In this study, aloe-emodin and emodin induced the changes of each of PKC isozymes in CH27 and H460 cells. 5. The decrease in the expression of PKC delta and epsilon may play a critical role in aloe-emodin- and emodin-induced apoptosis in CH27 and H460 cells. 6. The present study also demonstrated that PKC stimulation occurs at a site downstream of caspase-3 in the emodin-mediated apoptotic pathway.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects and mechanisms of aloe-emodin on cell death in human lung squamous cell carcinoma.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Nov 23;431(3):287-95. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01467-4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11730720
-
Signaling pathway for aloe-emodin-induced apoptosis in human H460 lung nonsmall carcinoma cell.Int J Cancer. 2003 Aug 10;106(1):26-33. doi: 10.1002/ijc.11185. Int J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12794753
-
Effects and mechanisms of emodin on cell death in human lung squamous cell carcinoma.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Sep;134(1):11-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704205. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11522592 Free PMC article.
-
Aloe-emodin modulates PKC isozymes, inhibits proliferation, and induces apoptosis in U-373MG glioma cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2004 Dec 20;4(14):1775-84. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2004.07.012. Int Immunopharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15531293
-
The Activity of 1,8-Dihydroanthraquinone Derivatives in Nervous System Cancers.Molecules. 2024 Dec 19;29(24):5989. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245989. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39770078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rottlerin potentiates camptothecin-induced cytotoxicity in human hormone refractory prostate cancers through increased formation and stabilization of topoisomerase I-DNA cleavage complexes in a PKCδ-independent pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Jul 1;84(1):59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.03.023. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22490701 Free PMC article.
-
Aloe-emodin Attenuates Staphylococcus aureus Pathogenicity by Interfering With the Oligomerization of α-Toxin.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 May 15;9:157. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00157. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31157174 Free PMC article.
-
Aloe-Emodin Influence on the Lysosomal Compartment of Hela Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017 Dec 29;18(12):3273-3279. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.12.3273. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017. PMID: 29286219 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of potential targets of aloe-emodin in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma using network pharmacology combined with bioinformatics.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 4;16(1):464. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02215-w. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40186059 Free PMC article.
-
Emodin induces apoptosis of human cervical cancer hela cells via intrinsic mitochondrial and extrinsic death receptor pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2013 Jul 16;13(1):71. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-13-71. Cancer Cell Int. 2013. PMID: 23866157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ASHKENAZI A., DIXIT V.M. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science. 1998;281:1305–1308. - PubMed
-
- BASU A. The potential of protein kinase C as a target for anticancer treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1993;59:257–280. - PubMed
-
- BASU A., AKKARAJU G.R. Regulation of caspase activation and cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-induced cell death by protein kinase C. Biochem. 1999;38:4245–4251. - PubMed
-
- BIALIK S., CRYNS V.L., DRINCIC A., MIYATA S., WOLLOWICK A.L., SRINIVASAN A., KITSIS R.N. The mitochondrial apoptotic pathway is activated by serum and glucose deprivation in cardiac myocytes. Circ. Res. 1999;85:403–414. - PubMed
-
- BOSSY-WETZEL E., GREEN D.R. Caspases induced cytochrome c release from mitochondria by activating cytosolic factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:17484–17490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

