Failure to induce enhanced protection against tuberculosis by increasing T-cell-dependent interferon-gamma generation
- PMID: 11683955
- PMCID: PMC1783293
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01305.x
Failure to induce enhanced protection against tuberculosis by increasing T-cell-dependent interferon-gamma generation
Abstract
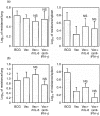
We evaluated the use of recombinant human interleukin-6 (rhIL-6) and a monoclonal antibody specific for interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) as co-adjuvants in a subunit vaccine against tuberculosis consisting of the culture filtrate proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (ST-CF) emulsified in the adjuvant dimethyl-dioctadecylammonium bromide (DDA). Both the addition of rhIL-6 and the neutralization of IFN-gamma resulted in an increased T helper type 1 (Th1) response characterized by enhanced IFN-gamma production and cell proliferation. Nevertheless, this did not result in the enhancement of protection against either an intravenous or an aerosol M. tuberculosis challenge. Our data stress the need to identify further correlates of protection in addition to IFN-gamma production to screen vaccines against tuberculosis infection.
Figures


References
-
- Jouanguy E, Döffinger R, Dupuis S, Pallier A, Altare F, Casanova J-L. IL-12 and IFN-γ in host defense against mycobacteria and salmonella in mice and men. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999;11:346–51. 10.1016/s0952-7915(99)80055-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Agger EM, Andersen P. Tuberculosis subunit vaccine development: on the role of interferon-γ. Vaccine. 2001:2298–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

