Effect of a short-term in vitro exposure to the marine toxin domoic acid on viability, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, matrix metalloproteinase-9 and superoxide anion release by rat neonatal microglia
- PMID: 11686853
- PMCID: PMC59507
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2210-1-7
Effect of a short-term in vitro exposure to the marine toxin domoic acid on viability, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, matrix metalloproteinase-9 and superoxide anion release by rat neonatal microglia
Abstract
Background: The excitatory amino acid domoic acid, a glutamate and kainic acid analog, is the causative agent of amnesic shellfish poisoning in humans. No studies to our knowledge have investigated the potential contribution to short-term neurotoxicity of the brain microglia, a cell type that constitutes circa 10% of the total glial population in the brain. We tested the hypothesis that a short-term in vitro exposure to domoic acid, might lead to the activation of rat neonatal microglia and the concomitant release of the putative neurotoxic mediators tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), matrix metalloproteinases-2 and-9 (MMP-2 and -9) and superoxide anion (O2-).
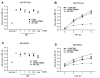
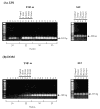
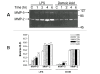
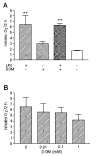
Results: In vitro, domoic acid [10 microM-1 mM] was significantly neurotoxic to primary cerebellar granule neurons. Although neonatal rat microglia expressed ionotropic glutamate GluR4 receptors, exposure during 6 hours to domoic acid [10 microM-1 mM] had no significant effect on viability. By four hours, LPS (10 ng/mL) stimulated an increase in TNF-alpha mRNA and a 2,233 % increase in TNF-alpha protein In contrast, domoic acid (1 mM) induced a slight rise in TNF-alpha expression and a 53 % increase (p < 0.01) of immunoreactive TNF-alpha protein. Furthermore, though less potent than LPS, a 4-hour treatment with domoic acid (1 mM) yielded a 757% (p < 0.01) increase in MMP-9 release, but had no effect on MMP-2. Finally, while PMA (phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate) stimulated O2- generation was elevated in 6 hour LPS-primed microglia, a similar pretreatment with domoic acid (1 mM) did not prime O2- release.
Conclusions: To our knowledge this is the first experimental evidence that domoic acid, at in vitro concentrations that are toxic to neuronal cells, can trigger a release of statistically significant amounts of TNF-alpha and MMP-9 by brain microglia. These observations are of considerable pathophysiological significance because domoic acid activates rat microglia several days after in vivo administration.
Figures


References
-
- Lassmann H, Schmied M, Vass K, Hickey WF. Bone marrow derived elements and resident microglia in brain inflammation. GLIA. 1993;7:19–24. - PubMed
-
- Mayer AM. Therapeutic implications of microglia activation by lipopolysaccharide and reactive oxygen species generation in septic shock and central nervous system pathologies: a review. Medicina (B Aires) 1998;58:377–385. - PubMed
-
- Perry VH, Gordon S. Macrophages and the nervous system. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;125:203–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

