Antidepressants versus psychological treatments and their combination for bulimia nervosa
- PMID: 11687197
- PMCID: PMC6999807
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003385
Antidepressants versus psychological treatments and their combination for bulimia nervosa
Abstract
Background: Psychotherapeutic approaches, mainly cognitive behavior therapy, and antidepressant medication are the two treatment modalities that have received most support in controlled outcome studies of bulimia nervosa.
Objectives: The primary objective was to conduct a systematic review of all RCTs comparing antidepressants with psychological approaches or comparing their combination with each single approach for the treatment of bulimia nervosa.
Search strategy: (1) electronic searches of MEDLINE (1966 to December 2000), EMBASE (1980-December 2000), PsycLIT (to December 2000), LILACS & SCISEARCH (to 1999) (2) the Cochrane Register of Controlled Trials and the Cochrane Depression, Anxiety and Neurosis Group Register - ongoing (3) handsearches of the references of all identified trials (4) contact with the pharmaceutical companies and the principal investigator of each included trial (5) handsearch of the International Journal of Eating Disorders - ongoing
Inclusion criteria: every randomized controlled trial in which antidepressants were compared with psychological treatments or the combination of antidepressants with psychological approaches was compared to each treatment alone, to reduce the symptoms of bulimia nervosa in patients of any age or gender. Quality criteria: reports were considered adequate if they were classified as A or B according to the Cochrane Manual.
Data collection and analysis: Data were extracted independently by two reviewers for each included trial. The main outcome for efficacy was full remission of bulimic symptoms, defined as 100% reduction in binge or purge episodes from baseline to endpoint. Dichotomous data was evaluated by the relative risks and 95% confidence intervals around this measure, based on the random effects model; continuous data was evaluated by the average difference and the 95% confidence interval. Number needed to treat (NNT) and number needed to harm (NNH) were calculated using the inverse of the absolute risk reduction.
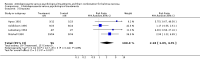
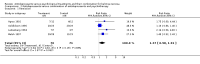
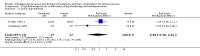
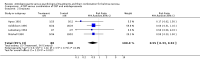
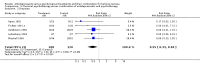
Main results: Five trials were included in comparison one (antidepressants versus psychological treatments), five in comparison two (antidepressants versus the combination) and seven in comparison three (psychological treatments versus the combination). Remission rates were 20% for single antidepressants compared to 39% for single psychotherapy (DerSimonian-Laird Relative Risk = 1.28; 95% Confidence Interval = 0.98;1.67). Dropout rates were higher for antidepressants than for psychotherapy (DerSimonian-Laird Relative Risk = 2.18; 95% Confidence Interval = 1.09;4.35). The NNH for a mean treatment duration of 17.5 weeks was 4 (95% confidence interval = 3;11). Comparison two found remission rates of 42% for the combination versus 23% for antidepressants (DerSimonian-Laird Relative Risk = 1.38; 95% Confidence Interval = 0.98;1.93). Comparison three showed a 36% pooled remission rate for psychological approaches compared to 49% for the combination (DerSimonian-Laird Relative Risk = 1.21; 95% Confidence Interval = 1.02;1.45). The NNT for a mean treatment duration of 15 weeks was 8 (95% Confidence Interval = 4;320). Dropout rates were higher for the combination compared to single psychological treatments (DerSimonian-Laird Relative Risk = 0.57; 95% Confidence Interval = 0.38;0.88). The NNH was 7 (95% Confidence Interval = 4;21).
Reviewer's conclusions: Using a more conservative statistical approach, combination treatments were superior to single psychotherapy. This was the only statistically significant difference between treatments. The number of trials might be insufficient to show the statistical significance of a 19% absolute risk reduction in efficacy favouring psychotherapy or combination treatments over single antidepressants. Psychotherapy appeared to be more acceptable to subjects. When antidepressants were combined to psychological treatments, acceptability of the latter was significantly reduced.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
JB has received fees from Janssen‐Cilag Farmaceutica, Brazil. PH has received supprot to attend conferences and meetings from Pfizer PTY Ltd, Solvay Pharmaceuticals and Bristol‐Myers Squibb Pharmaceuticals.
Figures














Comment in
-
Review: psychological treatment is as effective as antidepressants for bulimia nervosa, but a combination is best.ACP J Club. 2002 May-Jun;136(3):107. doi: 10.7326/acpjc-2002-136-3-107. ACP J Club. 2002. PMID: 11985448 No abstract available.
-
Review: psychological treatment is as effective as antidepressants for bulimia nervosa, but a combination is best.Evid Based Ment Health. 2002 Aug;5(3):74-5. Evid Based Ment Health. 2002. PMID: 12180442 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Agras 1992 {published data only}
-
- Agras WS, Rossiter EM, Arnow B, Schneider JA, Telch CF, Raeburn SD, et al. Pharmacologic and cognitive‐behavioral treatment for bulimia nervosa: a controlled comparison. American Journal of Psychiatry 1992;149(1):82‐7. - PubMed
Fichter 1991 a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fichter MM, Leibl K, Rief W, Brunner E, Schmidt‐Auberger S, Engel RR. Fluoxetine versus placebo: a double blind study with bulimic inpatients udergoing intensive psychotherapy. Pharmacopsychiatry 1991;24:1‐7. - PubMed
Goldbloom 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Goldbloom DS, Olmsted MP, Davies R, Shaw B. A randomized control trial of fluoxetine and cognitive behavioural therapy for bulimia nervosa: short‐term outcome. Behavioral Research and Therapy 1997;35(9):803‐11. - PubMed
Leitenberg 1994 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Leitenberg H, Rosen JC, Wolf J, Vara LS, Detzer MJ, Srebnik D. Comparison of cognitive‐behavior therapy and desipramine in the treatment of bulimia nervosa. Behavioral Research and Therapy 1994;32(1):37‐45. - PubMed
Mitchell 1990 {published data only}
-
- Mitchell JE, Pyle RL, Eckert ED, Hatsukami D, Pomeroy C, Zimmerman R. A comparison study of antidepressants and structured intensive group psychoterapy in the treatment of bulimia nervosa. Archives of General Psychiatry 1990;47(2):149‐57. - PubMed
Russell 1995 b {published data only}
-
- Beumont PJ, Russell JD, Touyz SW, Buckley C, Lowinger K, Talbot P, et al. Intensive nutritional counselling in bulimia nervosa: a role for supplementation with fluoxetine?. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 1997;31(4):514‐24. - PubMed
Walsh 1997 {published data only}
-
- Walsh BT, Wilson GT, Loeb KL, Devlin MJ, Pike KM, Roose SP, Fleiss J, Waternaux C. Medication and psychotherapy in the treatment of bulimia nervosa. American Journal of Psychiatry 1997;154(4):523‐31. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Agras 1987 {published data only}
-
- Agras WS, Dorian B, Kirkley BG, Arnow B, Bachman J. Imipramine in the treatment of bulimia: a double ‐blind controlled study. International Journal of Eating Disorders 1987;6:29‐38.
Alger 1991 {published data only}
-
- Alger AS, Shwalberg MD, Bigaouette JM, Michalek AV, Howard LJ. Effect of a tricyclic antidepressant and opiate antagonist on binge‐eating behavior in normoweight bulimic and obese, binge‐eating subjects. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1991;53(4):865‐71. - PubMed
Barlow 1988 {published data only}
-
- Barlow J, Blouin J, Blouin A, Perez E. Treatment of bulimia with desipramine: a double‐blind crossover study. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 1988;33(2):129‐33. - PubMed
Blouin 1988 {published data only}
-
- Blouin AG, Blouin JH, Perez EL, Bushnik T, Zuro C, Mulder E. Treatment of bulimia with fenfluramine and desipramine. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1988;8(4):261‐9. - PubMed
Box 1983 {published data only}
-
- Box J, Arnold E, Smeltzer DJ. Protriptyline weight loss in compulsive eaters: a placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Psychiatric Treatment and Evaluation 1983;5(4):387‐91.
FBNCSG 1992 {published data only}
-
- Fluoxeting Bulimia Nervosa Collaborative Study Group. Fluoxetine in the treatment of bulimia nervosa. Archives of General Psychiatry 1992;49(2):139‐47. - PubMed
Fichter 1991 {published data only}
-
- Fichter MM, Krüger R, Rief W, Holland R, Döhne J. Fluvoxamine in prevention of relapse in bulimia nervosa: effects on eating specific psychopathology. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1996;16:9‐18. - PubMed
-
- Fichter MM, Leibl K, Rief W, Brunner E, Schmidt‐Auberger S, Engel RR. Fluoxetine versus placebo: a double blind study with bulimic inpatients udergoing intensive psychotherapy.. Pharmacopsychiatry 1991;24:1‐7. - PubMed
Horne 1988 {published data only}
-
- Horne RL, Ferguson JM, Pope HG Jr, Hudson JI, Lineberry CG, Ascher J, et al. Treatment of bulimia with bupropion: a multicenter controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1988;49(7):262‐6. - PubMed
Hughes 1986 a {published data only}
-
- Hughes PL, Wells LA, Cunningham CJ, Ilstrup DM. Treating bulimia with desipramine. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Archives of General Psychiatry 1986;43(2):182‐6. - PubMed
Kanerva 1994 {published data only}
-
- Kanerva R, Rissanen A, Sarna S. Fluoxetine in the treatment of anxiety, depressive symptoms, and eating‐related symptoms in bulimia nervosa. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 1994;49(4):237‐42.
Kennedy 1986 {published data only}
-
- Kennedy S, Piran N, Garfinkel PE. Isocarboxazide in the treatment of bulimia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1986;143(11):1495‐6. - PubMed
Kennedy 1988 {published data only}
-
- Kennedy SH, Piran N, Warsh JJ, Prendergast P, Mainprize E, Whynot C, et al. A trial of isocarboxazid in the treatment of bulimia nervosa. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1988;8(6):391‐6. - PubMed
Kennedy 1993 {published data only}
-
- Kennedy SH, Goldbloom DS, Ralevski E, Davis C, D’Souza JD, Lofchy JE. Is there a role for selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy in bulimia nervosa? A placebo‐controlled trial of braforamin. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1993;13(6):415‐22. - PubMed
Marcus 1990 {published data only}
-
- Marcus MD, Wing RR, Ewing L, Kern E, McDermott M, Gooding W. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial of fluoxetine plus behavioral modification in the treatment of obese binge‐eaters. American Journal of Psychiatry 1990;147(7):876‐81. - PubMed
Margittai 1987 {published data only}
-
- Margittai KJ, Blouin A, Perez E. A study of dropouts in psychopharmacological research with bulimics. International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine 1987;16(4):297‐304. - PubMed
McCann 1990 {published data only}
-
- McCann UD, Agras WS. Successful treatment of nonpurging bulimia nervosa with desipramine: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. American Journal of Psychiatry 1990;147(11):1509‐13. - PubMed
Mitchell 1984 {published data only}
-
- Mitchell JE, Groat R. A placebo‐controlled double‐blind trial of amitriptyline in bulimia.. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1984;4(4):186‐93. - PubMed
Mitchell 1987 b {published data only}
-
- Pyle RL, Mitchell JE, Eckert ED, Hatsukami D, Pomeroy C, Zimmerman R. Maintenance treatment and 6‐month outcome for bulimic patients who respond to initial treatment. American Journal of Psychiatry 1990;147(7):871‐5. - PubMed
Pope 1983 {published data only}
-
- Pope HG, Hudson JI Jonas JM, Yurgelun‐Todd D. Antidepressant treatment of bulimia: a two‐year follow‐up study. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1985;5(6):320‐7. - PubMed
-
- Pope HG, Hudson JI, Jonas JM, Yurgelum‐Todd D. Bulimia treated with imipramine. American Journal of Psychiatry 1983;140(5):554‐8. - PubMed
Pope 1989 {published data only}
-
- Pope HG, Keck PE, McElroy S, Hudson JI. A placebo‐controlled study of trazodone in bulimia nervosa. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1989;9(4):254‐9. - PubMed
Price 1987 {published data only}
-
- Price W, Massood RB, Youngstrom O. Antidepressant drug therapy for bulimia: Current status revisited. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1987;48(9):385. - PubMed
Rothschild 1994 {published data only}
-
- Rothschild R, Quitkin HM, Quiktin FM, Stewart JW, Ocepek‐Welikson K, McGrath PJ, Tricamo E. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled comparison of phenelzine and imipramine in the treatment of bulimia in atypical depressives. International Journal of Eating Disorders 1994;15:1‐9. - PubMed
Sabine 1983 {published data only}
Scrimali 1994 {published data only}
-
- Scrimali T, Grimali L, Corriere A, Grasso F, Frisone MF. Fluoxetine in the pharmacological treatment of bulimia nervosa [La fluoxetina nel tratamento farmacologico della bulimia nervosa]. Rivista di Psichiatria 1994;29(3):171‐7.
Walsh 1984 {published data only}
-
- Walsh T, Stewart JW, Roose, Gladis M, Glassman AH. Treatment of bulimia with phenelzine. Archives of General Psychiatry 1984;41(11):1105‐9. - PubMed
Walsh 1985 {published data only}
-
- Walsh BT, Stewart JW, Roose SP, Gladis M, Glassman AH. A double‐blind trial of phenelzine in bulimia. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1985;19(2‐3):485‐9. - PubMed
Walsh 1991 a {published data only}
-
- Walsh BT, Hadigan CM, Devlin MJ, Gladis M, Roose SP. Long‐term outcome of antidepressant treatment for bulimia nervosa.. American Journal of Psychiatry 1991;148(9):1206‐12. - PubMed
-
- Walsh T, Hadigan CM, Wong LM. Increased pulse and blood pressure associated with desipramine treatment of bulimia nervosa. Journal of Clinical Psychopharamacology 1992;12(3):163‐8. - PubMed
Wheadon 1992 {published data only}
-
- Goldstein DJ, Wilson MG, Thomson VL, Potvin JH, Rampey AH Jr. Long‐term fluoxetine treatment of bulimia nervosa. British Journal of Psychiatry 1995;166:660‐666. - PubMed
Additional references
Advokat 1995
-
- Advokat C, Kutlesic V. Pharmacotherapy of the eating disorders: a commentary. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 1995;19(1):59‐66. - PubMed
APA 1980
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders (DSM‐III). 3rd Edition. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1980.
APA 1987
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders (DSM‐III‐R). 3rd Edition. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1987.
APA 1994
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders (DSM‐IV). 4th Edition. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1994.
Bacaltchuk 2000 a
-
- Bacaltchuk J, Hay P, Mari JJ. Antidepressants versus placebo for the treatment of bulimia nervosa: a systematic review. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 2000;34(2):310‐7. - PubMed
Buchan 1997
-
- Buchan IE. Arcus QuickStat Biomedical for windows. 1. Cambridge UK: Addison Wesley Longman Limited trading as Research Solutions, 1997.
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power for the Behavioral Sciences. 2nd Edition. Hillsdale NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum, 1988.
Cook 1995
Corcos 1996
-
- Corcos M, Flament M, Atger F, Jeammet PH. Pharmacological treatment of bulimia [Traitement pharmacologique de la bulimie]. Encephale 1996;22(2):133‐42. - PubMed
Cucherat 1997
-
- Cucherat M. Meta‐analyse des essais therapeutiques. Paris: Masson, 1997.
DerSimonian 1996
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;7(3):177‐88. - PubMed
Fairburn 1991
-
- Fairburn CG, Marcus MD, Wilson GT. Cognitive behavioural therapy for treatment of bulimia nervosa. In: Fairburn CG, Wilson GT editor(s). Binge eating: Nature, assessment and treatment. New York: Guilford Press, 1993:361‐404.
Foreyt 1996
-
- Foreyt JP, Poston WS, Goodrick GK. Future directions in obesity and eating disorders. Addictive Behaviours 1996;21(6):767‐78. - PubMed
Hay 2000
-
- Hay PJ, Bacaltchuk J. Psychotherapy for bulimia nervosa and binge eating. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2000, Issue 4. - PubMed
Hedges 1985
-
- Hedges LV, Olkin I. Statistical methods for meta‐analysis. San Diego CA: Academic Press, 1985.
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad A, Moore A, Carrol D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavanagh DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17(1):1‐12. - PubMed
Light 1984
-
- Light RJ, Pillemer DB. Summing up: The Science of Revieweing Research. Cambridge MA: Harvard University Press, 1984.
Lima 1998
-
- Lima MS, Montcrieff J. A comparison of drugs versus placebo for the treatment of dysthymia: a systematic review. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1998, Issue 2. - PubMed
Mitchell 1991
-
- Mitchell JE, Specker SM, Zwaan M. Comorbidity and medical complications of bulimia nervosa. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1991;52(Suppl):13‐20. - PubMed
Mulrow 1996
-
- Mulrow CD, Oxman AD. Cochrane Collaboration Handbook. Oxford: Update Software, 1996.
Rosenthal 1979
-
- Rosenthal R. The "file drawer problem" and the tolerance for null results. Psychological Bulletin 1979;86(3):638‐41.
Russell 1979
-
- Russell GF. Bulimia nervosa: an ominous variant of anorexia nervosa. Psychological Medicine 1979;9(3):429‐48. - PubMed
Sackett 1994
-
- Sackett DL. Cochrane Collaboration Handbook. Oxford: Update Software, 1994.
Schultz 1995
-
- Schultz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408‐412. - PubMed
Shaw 1990
-
- Shaw B, Garfinkel PE. Research problems in the eating disorders. International Journal of Eating Disorders 1990;9(5):545‐55.
Thomson 1995
-
- Thomson SG. Why sources of heterogeneity in meta‐analysis should be investigated. In: Chalmers I, Altman DG editor(s). Systematic Reviews. Bristol: BMJ Publishing, 1995:48‐63.
Walsh 1997 a
-
- Walsh BT, Wilson GT, Loeb KL, Devlin MJ, Pike KM, Roose SP, et al. Medication and psychotherapy in the treatment of bulimia nervosa. American Journal of Psychiatry 1997;154(4):523‐31. - PubMed
WHO 1992
-
- World Health Organisation. The ICD‐10 Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders. Clinical Descriptions and diagnostic guidelines. Geneva: WHO, 1992.
Wilson 1995
-
- Wilson GT. Empirically validated treatments as a basis for clinical practice. Problems and prospects. In: Hayes SC, Follette VM, Risley T, Dawes RD, Grady K editor(s). Scientific standards of psychological practice: Issues and recommendations. Reno NV: Context Press, 1995:163‐96.
Wolfe 1995
-
- Wolfe BE. Dimensions of response to antidepressant in bulimia nervosa: a review. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing 1995;9(3):111‐21. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Bacaltchuk 1999
-
- Bacaltchuk J, Trefiglio RP, Oliveira IR, Lima MS, Mari JJ. Antidepressants versus psychotherapy for bulimia nervosa: a systematic review. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics 1999;24(1):23‐31. - PubMed
Bacaltchuk 2000
-
- Bacaltchuk J, Trefiglio RP, Oliveira IR, Hay P, Lima MS, Mari JJ. Combination of antidepressants and psychological treatments for bulimia nervosa: a systematic review. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2000;101(4):256‐64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

