Antibody responses of cattle immunized with the Tf190 adhesin of Tritrichomonas foetus
- PMID: 11687450
- PMCID: PMC96236
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.6.1120-1125.2001
Antibody responses of cattle immunized with the Tf190 adhesin of Tritrichomonas foetus
Abstract
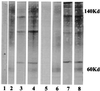
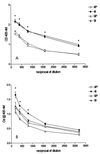
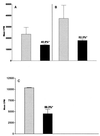
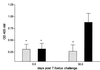
The antibody response patterns of cattle after subcutaneous and intranasal immunizations with adhesin Tf190 of Tritrichomonas foetus were investigated. Reactions of antibody from cattle parenterally immunized with Tf190 revealed antigen specificity and Tf190 sensitization in the majority of the animals, as determined by Western blotting. The results also demonstrated strong preimmune immunoglobulin G2 (IgG2) binding to T. foetus antigens not seen in IgG1 profiles. Subcutaneous injections of Tf190 resulted in significant (P < 0.05) increases in serum IgG1 and IgG2 titers over time, as determined by parasite specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Immune sera also significantly inhibited parasite adhesion to mammalian cell lines compared to the level of inhibition obtained with preimmune sera (P < 0.05). Intranasal immunization with Tf190 failed to produce measurable parasite-specific antibody in serum; however, this immunization route did result in significant (P < 0.05) increases in parasite-specific IgA titers in cervical mucus secretions from immunized animals that were more resistant to intravaginal challenge with T. foetus than controls. These results suggest that systemic immunization with Tf190 results in serum antibody production and antiparasitic adhesin antibodies. Additionally, the results of challenge experiments with intranasally immunized animals suggests that Tf190 primes protective immune responses that lead to lower rates of infection among these animals.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antigen-specific T-cell responses in cattle immunized with antigens of Tritrichomonas foetus.J Parasitol. 2001 Oct;87(5):1040-8. doi: 10.1645/0022-3395(2001)087[1040:ASTCRI]2.0.CO;2. J Parasitol. 2001. PMID: 11695362
-
Immunization of virgin cows with surface antigen TF1.17 of Tritrichomonas foetus.Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1385-94. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1385-1394.1993. Infect Immun. 1993. PMID: 8454340 Free PMC article.
-
Specific antibodies in serum and vaginal mucus of heifers inoculated with a vaccine containing Tritrichomonas foetus.Am J Vet Res. 1995 Apr;56(4):454-9. Am J Vet Res. 1995. PMID: 7785821
-
Host-parasite interaction in bovine infection with Tritrichomonas foetus.Microbes Infect. 1999 Aug;1(10):807-16. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(99)80083-5. Microbes Infect. 1999. PMID: 10816086 Review.
-
Immunity to infections in the lower genital tract of bulls.J Reprod Immunol. 2011 Apr;89(1):55-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2011.02.002. Epub 2011 Apr 6. J Reprod Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21474188 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic Review of Vaccine Strategies Against Tritrichomonas foetus Infection in Cattle: Insights, Challenges, and Prospects.Parasite Immunol. 2025 Jan;47(1):e70003. doi: 10.1111/pim.70003. Parasite Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39838701 Free PMC article.
-
A new inactivated Tritrichomonas foetus vaccine that improves genital clearance of the infection and calving intervals in cattle.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Oct 6;9:1005556. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1005556. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36277069 Free PMC article.
-
Fulminant Tritrichomonas foetus 'feline genotype' infection in a 3-month old kitten associated with viral co-infection.Vet Parasitol. 2019 Mar;267:17-20. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2018.12.007. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Vet Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 30878079 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative aspects of immunity and vaccination in human and bovine trichomoniasis: a review.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2016 Jan;48(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s11250-015-0909-1. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2016. PMID: 26424377 Review.
-
Bovine neutrophils kill the sexually-transmitted parasite Tritrichomonas foetus using trogocytosis.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Apr;48(2):865-875. doi: 10.1007/s11259-023-10260-5. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 37968413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbit B, Ball L. Diagnosis of trichomoniasis in pregnant cows by culture of cervico-vaginal mucus. Theriogenology. 1978;9:616–619.
-
- Anderson M L, BonDurant R H, Corbeil R R, Corbeil L B. Immune and inflammatory responses to reproductive tract infection with Tritrichomonas foetus in immunized and control heifers. J Parasitol. 1996;82:594–600. - PubMed
-
- Burgess D E. Tritrichomonas foetus: preparation of monoclonal antibodies with effector function. Exp Parasitol. 1986;62:266–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

