Pre-clinical validation of a novel, highly sensitive assay to detect PML-RARalpha mRNA using real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction
- PMID: 11687597
- PMCID: PMC1906965
- DOI: 10.1016/s1525-1578(10)60665-4
Pre-clinical validation of a novel, highly sensitive assay to detect PML-RARalpha mRNA using real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction
Abstract
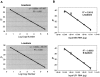
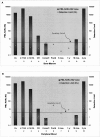
We have developed a sensitive and quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay for detection of PML-RARalpha, the fusion oncogene present as a specific marker in >99% of cases of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). The assay is linear over at least 5 orders of magnitude of input DNA or RNA, and detects as few as 4 copies of PML-RARalpha plasmid DNA. PML-RARalpha transcripts could be detected in mixtures containing 2 to 5 pg of RNA from fusion-containing cells in a background of 1 microg of RNA from PML-RARalpha-negative cells. Using 1.0 to 2.5 microg of input RNA, the sensitivity of the assay was between 10(-5) and 10(-6). Furthermore, determination of GAPDH copy number in each reaction allowed an accurate assessment of sample-to-sample variation in RNA quality and reaction efficiency, with consequent definition of a detection limit for each sample assayed. Using an internal calibrator, assay precision was high, with coefficients of variation between 10 and 20%. An interlaboratory study using coded samples demonstrated excellent reproducibility and high concordance between laboratories. This assay will be used to test the hypothesis that sensitive and quantitative measurement of leukemic burden, during or after therapy of APL, can stratify patients into discrete risk groups, and thereby serve as a basis for risk-adapted therapy in APL.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Feasibility and clinical significance of real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay of PML-RARalpha fusion transcript in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia.Hematol J. 2001;2(5):330-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.thj.6200128. Hematol J. 2001. PMID: 11920269
-
[Detection of PML/RARalpha gene transcripts in 46 newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia patients by real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Feb;15(1):1-5. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 17490509 Chinese.
-
[Improved RT-PCR for detection of PML/RARalpha fusion gene in rapid diagnosis of acute promyelocytic leukemia].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2003 Dec;11(6):587-90. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14706140 Chinese.
-
Acute promyelocytic leukaemia in patients originating in Latin America is associated with an increased frequency of the bcr1 subtype of the PML/RARalpha fusion gene.Br J Haematol. 2003 Aug;122(4):563-70. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2003.04480.x. Br J Haematol. 2003. PMID: 12899711 Review.
-
Understanding the molecular pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukemia.Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2014 Mar;27(1):3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.beha.2014.04.006. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2014. PMID: 24907012 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced degradation of dihydrofolate reductase through inhibition of NAD kinase by nicotinamide analogs.Mol Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;83(2):339-53. doi: 10.1124/mol.112.080218. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Mol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23197646 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time PCR for monitoring minimal residual disease and chimerism in patients after allogeneic transplantation.Int J Hematol. 2002 Aug;76 Suppl 2:204-5. doi: 10.1007/BF03165118. Int J Hematol. 2002. PMID: 12430926 Review.
-
IL-33 induces IL-9 production in human CD4+ T cells and basophils.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21695. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021695. Epub 2011 Jul 6. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21765905 Free PMC article.
-
O-GlcNAcylation promotes migration and invasion in human ovarian cancer cells via the RhoA/ROCK/MLC pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Apr;15(4):2083-2089. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6244. Epub 2017 Feb 24. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28259907 Free PMC article.
-
Relapse of acute promyelocytic leukemia with PML-RARalpha mutant subclones independent of proximate all-trans retinoic acid selection pressure.Leukemia. 2006 Apr;20(4):556-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404118. Leukemia. 2006. PMID: 16437139 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Look AT: Oncogenic transcription factors in the human acute leukemias. Science 1997, 278:1059-1064 - PubMed
-
- Nucifora G, Larson RA, Rowley JD: Persistence of the 8;21 translocation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia type M2 in long-term remission. Blood 1993, 82:712-715 - PubMed
-
- Tobal K, Liu Yin JA: RT-PCR method with increased sensitivity shows persistence of PML-RARα fusion transcripts in patients in long-term remission of APL. Leukemia 1998, 12:1349-1354 - PubMed
-
- Jurlander J, Caligiuri MA, Ruutu T, Baer MR, Strout MP, Oberkircher AR, Hoffmann L, E.D B, Frei-Lahr DA, Christiansen NP, Block AW, Knuutila S, Herzig GP, Bloomfield CD: Persistence of the AML1/ETO fusion transcript in patients treated with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for t(8;21) leukemia. Blood 1996, 88:2183-2191 - PubMed
-
- Slack JL, Gallagher RE: The molecular biology of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Treat Res 1999, 99:75-124 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

