Validation of denaturing high performance liquid chromatography as a rapid detection method for the identification of human INK4A gene mutations
- PMID: 11687599
- PMCID: PMC1906963
- DOI: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60667-8
Validation of denaturing high performance liquid chromatography as a rapid detection method for the identification of human INK4A gene mutations
Abstract
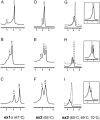
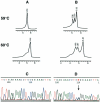
The incidence of melanoma is increasing rapidly in western countries. Genetic predisposition in familial and in some sporadic melanomas has been associated with the presence of INK4A gene mutations. To better define the risk for developing sporadic melanoma based on genetic and environmental interactions, large groups of cases need to be studied. Mutational analysis of genes lacking hot spots for sequence variations is time consuming and expensive. In this study we present the application of denaturing high performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) for screening of mutations. Exons 1alpha, 2, and 3 were amplified from 129 samples and 13 known mutants, yielding 347 products that were examined at different temperatures. Forty-two of these amplicons showed a distinct non-wild-type profile on the chromatogram. Independent sequencing analysis confirmed 16 different nucleotide variations in Leu32Pro; Ile49Thr; 88 del G; Gln50Arg; Arg24Pro; Met53Ile; Met53Thr; Arg58stop; Pro81Leu; Asp84Ala; Arg80stop; Gly101Trp; Val106Val; Ala148Thr; and in positions (-2) in intron 1 (C --> T); and in the 3' UTR, nucleotide 500 (C --> G). No false negatives or false positives were obtained by DHPLC in samples with mutations or polymorphisms. We conclude that the DHPLC is a fast, sensitive, cost-efficient, and reliable method for the scanning of INK4A somatic or germline mutations and polymorphisms of large number of samples.
Figures
References
-
- Rigel DS, Carucci JA: Malignant melanoma: prevention, early detection, and treatment in the 21st century. CA Cancer J Clin 2000, 50:215–236; 237–240 - PubMed
-
- Cohn-Cedermark G, Mansson-Brahme E, Rutqvist LE, Larsson O, Johansson H, Ringborg U: Trends in mortality from malignant melanoma in Sweden, 1970–1996. Cancer 2000, 89:348-355 - PubMed
-
- Hara H, Walsh N, Yamada K, Jimbow K: High plasma level of a eumelanin precursor, 6-hydroxy-5-methoxyindole-2-carboxylic acid, as a prognostic marker for malignant melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 1994, 102:501-505 - PubMed
-
- DiFronzo LA, Wanek LA, Elashoff R, Morton DL: Increased incidence of second primary melanoma in patients with a previous cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol 1999, 6:705-711 - PubMed
-
- Serraino D, Fratino L, Gianni W, Campisi C, Pietropaolo M, Trimarco G, Marigliano V: Epidemiological aspects of cutaneous malignant melanoma. Oncol Rep 1998, 5:905-909 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

