The expression of the gamma subunit of Na-K-ATPase is regulated by osmolality via C-terminal Jun kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent mechanisms
- PMID: 11687620
- PMCID: PMC60885
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.231309198
The expression of the gamma subunit of Na-K-ATPase is regulated by osmolality via C-terminal Jun kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent mechanisms
Abstract
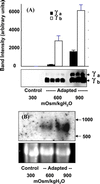
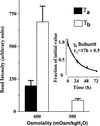
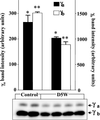
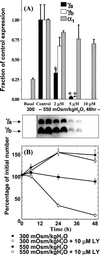
The alpha and beta subunits of Na-K-ATPase are up-regulated by hypertonicity in inner-medullary collecting duct cells adapted to survive in hypertonic conditions. We examined the regulation of the gamma subunit by hypertonicity. Although cultured inner-medullary collecting duct cells lacked the gamma subunits, both variants gamma(a) and gamma(b) were expressed in cells adapted to 600 and 900 mosmol/KgH(2)O. This expression was reversible with a half-time of 17.2 +/- 0.5 h. The message of the gamma subunit was absent in isotonic conditions and increased with higher tonicity in adapted cells. In acute experiments the appearance of the gamma subunit was found to be both time-dependent (> or =24 h) and osmolality-dependent (> or =500 mosmol/KgH(2)O). No induction was noted with urea and only minimal induction with mannitol. Increasing concentrations of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 resulted in a dose-dependent decrement in the expression of the gamma subunit with total abolition at 10 microM. This was associated with a decrease in cell viability as <20% survived the treatment with 10 microM of LY294002. Neither inhibition of extracellular response kinase nor p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibited osmotic induction of the gamma subunit. In contrast, cells transfected with a dominant negative c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2-APF construct displayed complete inhibition of the gamma subunit. Such cells have accelerated loss of viability in hypertonic conditions. This study describes the regulation of the gamma subunit of Na-K-ATPase by hypertonicity. This regulation is transcriptionally regulated and involves signaling mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 pathways.
Figures
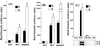
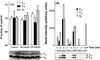
References
-
- Chemaberlin M E, Strange K. Am J Physiol. 1989;257:C159–C173. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Perez A, Burg M B. Physiol Rev. 1991;71:1081–1115. - PubMed
-
- Berl T, Siriwardana G, Ao L, Butterfield L M, Heasley L E. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:F305–F311. - PubMed
-
- Yancey P H, Burg M B. Am J Physiol. 1990;258:R198–R204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

