Enzyme interactions in heparan sulfate biosynthesis: uronosyl 5-epimerase and 2-O-sulfotransferase interact in vivo
- PMID: 11687650
- PMCID: PMC60811
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.241175798
Enzyme interactions in heparan sulfate biosynthesis: uronosyl 5-epimerase and 2-O-sulfotransferase interact in vivo
Abstract
The formation of heparan sulfate occurs within the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi complex-trans-Golgi network by the concerted action of several glycosyltransferases, an epimerase, and multiple sulfotransferases. In this report, we have examined the location and interaction of tagged forms of five of the biosynthetic enzymes: galactosyltransferase I and glucuronosyltransferase I, required for the formation of the linkage region, and GlcNAc N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1, uronosyl 5-epimerase, and uronosyl 2-O-sulfotransferase, the first three enzymes involved in the modification of the chains. All of the enzymes colocalized with the medial-Golgi marker alpha-mannosidase II. To study whether any of these enzymes interacted with each other, they were relocated to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by replacing their cytoplasmic N-terminal tails with an ER retention signal derived from the cytoplasmic domain of human invariant chain (p33). Relocating either galactosyltransferase I or glucuronosyltransferase I had no effect on the other's location or activity. However, relocating the epimerase to the ER caused a parallel redistribution of the 2-O-sulfotransferase. Transfected epimerase was also located in the ER in a cell mutant lacking the 2-O-sulfotransferase, but moved to the Golgi when the cells were transfected with 2-O-sulfotransferase cDNA. Epimerase activity was depressed in the mutant, but increased upon restoration of 2-O-sulfotransferase, suggesting that their physical association was required for both epimerase stability and translocation to the Golgi. These findings provide in vivo evidence for the formation of complexes among enzymes involved in heparan sulfate biosynthesis. The functional significance of these complexes may relate to the rapidity of heparan sulfate formation.
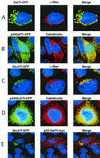
Figures





References
-
- Lindahl U, Kusche-Gullberg M, Kjellén L. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:24979–24982. - PubMed
-
- Shworak N W, Liu J A, Petros L M, Zhang L J, Kobayashi M, Copeland N G, Jenkins N A, Rosenberg R D. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:5170–5184. - PubMed
-
- Aikawa J, Grobe K, Tsujimoto M, Esko J D. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:5876–5882. - PubMed
-
- Habuchi H, Tanaka M, Habuchi O, Yoshida K, Suzuki H, Ban K, Kimata K. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:2859–2868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

