The interplay of matrix metalloproteinases, morphogens and growth factors is necessary for branching of mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 11688561
- PMCID: PMC2785713
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.128.16.3117
The interplay of matrix metalloproteinases, morphogens and growth factors is necessary for branching of mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
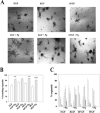
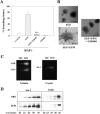
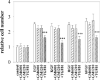
The mammary gland develops its adult form by a process referred to as branching morphogenesis. Many factors have been reported to affect this process. We have used cultured primary mammary epithelial organoids and mammary epithelial cell lines in three-dimensional collagen gels to elucidate which growth factors, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and mammary morphogens interact in branching morphogenesis. Branching stimulated by stromal fibroblasts, epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor 7, fibroblast growth factor 2 and hepatocyte growth factor was strongly reduced by inhibitors of MMPs, indicating the requirement of MMPs for three-dimensional growth involved in morphogenesis. Recombinant stromelysin 1/MMP3 alone was sufficient to drive branching in the absence of growth factors in the organoids. Plasmin also stimulated branching; however, plasmin-dependent branching was abolished by both inhibitors of plasmin and MMPs, suggesting that plasmin activates MMPs. To differentiate between signals for proliferation and morphogenesis, we used a cloned mammary epithelial cell line that lacks epimorphin, an essential mammary morphogen. Both epimorphin and MMPs were required for morphogenesis, but neither was required for epithelial cell proliferation. These results provide direct evidence for a crucial role of MMPs in branching in mammary epithelium and suggest that, in addition to epimorphin, MMP activity is a minimum requirement for branching morphogenesis in the mammary gland.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmed SA, Gogal RM, Jr, Walsh JE. A new rapid and simple non radioactive assay to monitor and determine the proliferation of lymphocytes: an alternative to [3H ]thymidine incorporation assay. J. Immunol. Methods. 1994;170:211–224. - PubMed
-
- Basbaum CB, Werb Z. Focalized proteolysis: spatial and temporal regulation of extracellular matrix degradation at the cell surface. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1996;8:731–738. - PubMed
-
- Berdichevsky F, Alford D, D' Souza B, Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Branching morphogenesis of human mammary epithelial cells in collagen gels. J. Cell Sci. 1994;107:3557–3568. - PubMed
-
- Bernfield M, Banerjee SD, Koda JE, Rapraeger AC. Remodelling of the basement membrane: morphogenesis and maturation. Ciba Found. Symp. 1984;108:179–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

